-
Články
- Vzdělávání
- Časopisy
Top články
Nové číslo
- Témata
- Kongresy
- Videa
- Podcasty
Nové podcasty
Reklama- Kariéra
Doporučené pozice
Reklama- Praxe
Twist1 Controls a Cell-Specification Switch Governing Cell Fate Decisions within the Cardiac Neural Crest
Neural crest cells are multipotent progenitor cells that can generate both ectodermal cell types, such as neurons, and mesodermal cell types, such as smooth muscle. The mechanisms controlling this cell fate choice are not known. The basic Helix-loop-Helix (bHLH) transcription factor Twist1 is expressed throughout the migratory and post-migratory cardiac neural crest. Twist1 ablation or mutation of the Twist-box causes differentiation of ectopic neuronal cells, which molecularly resemble sympathetic ganglia, in the cardiac outflow tract. Twist1 interacts with the pro-neural factor Sox10 via its Twist-box domain and binds to the Phox2b promoter to repress transcriptional activity. Mesodermal cardiac neural crest trans-differentiation into ectodermal sympathetic ganglia-like neurons is dependent upon Phox2b function. Ectopic Twist1 expression in neural crest precursors disrupts sympathetic neurogenesis. These data demonstrate that Twist1 functions in post-migratory neural crest cells to repress pro-neural factors and thereby regulate cell fate determination between ectodermal and mesodermal lineages.
Published in the journal: . PLoS Genet 9(3): e32767. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1003405
Category: Research Article
doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1003405Summary
Neural crest cells are multipotent progenitor cells that can generate both ectodermal cell types, such as neurons, and mesodermal cell types, such as smooth muscle. The mechanisms controlling this cell fate choice are not known. The basic Helix-loop-Helix (bHLH) transcription factor Twist1 is expressed throughout the migratory and post-migratory cardiac neural crest. Twist1 ablation or mutation of the Twist-box causes differentiation of ectopic neuronal cells, which molecularly resemble sympathetic ganglia, in the cardiac outflow tract. Twist1 interacts with the pro-neural factor Sox10 via its Twist-box domain and binds to the Phox2b promoter to repress transcriptional activity. Mesodermal cardiac neural crest trans-differentiation into ectodermal sympathetic ganglia-like neurons is dependent upon Phox2b function. Ectopic Twist1 expression in neural crest precursors disrupts sympathetic neurogenesis. These data demonstrate that Twist1 functions in post-migratory neural crest cells to repress pro-neural factors and thereby regulate cell fate determination between ectodermal and mesodermal lineages.
Introduction
Neural Crest Cells (NCCs) are multi-potent progenitor cells, which after delaminating from the dorsal lip of the neural tube and migrating throughout the developing embryo, can differentiate along either ectodermal or mesodermal lineages [1]–[4]. For example, a subset of NCCs, the cardiac NCCs (cNCCs) invades the aorticopulmonary cushions (APC) and septum (AoPS) of the developing cardiac outflow tract (OFT), the conduit through which blood exits the ventricles [5]–[8]. There, these cells assume a mesodermal identity, differentiating into connective tissue and smooth muscle and septating the pulmonary trunk and aorta to divide systemic and pulmonary circulation. Alternatively, the trunk, vagal, and sacral NCCs assume ectodermal identities, differentiating into the sympathetic, parasympathetic, and enteric neurons of the autonomic nervous system [9]. The transcriptional mechanisms that regulate NCC fate choice between these ectodermal and mesodermal lineages are not known. NCCs are specified along a rostro-caudal axis into distinct subpopulations that have limited capacity to change their cell fate [10]. However, both the cardiac and the rostral-most vagal neural crest originate at the same axial level (somites 1–3), suggesting that additional mechanisms of cell fate determination beyond axial specification are necessary to distinguish these ectodermal and mesodermal lineages. Indeed, both differentiating sympathetic neurons and cNCCs have been shown to respond to local secreted signaling cues, notably Bone Morphogenetic Proteins (BMPs), subsequently upregulating transcriptional effectors such as the Twist family bHLH proteins, Hand2 and Hand1, and initiating differentiation programs [11], [12]. The mechanisms that enable post-migratory NCCs to interpret these local signaling cues and to undergo either ectodermal or mesodermal differentiation programs are not understood.
In Drosophila, the transcription factor twist is essential for mesoderm development. In vertebrates; however, despite the evident requirement for Twist1 in the development of multiple mesodermally-derived organ systems, an analogous molecular mechanism by which Twist1 might control mesenchymal cell fate choice has not been defined [13]. Previously, we have shown that Twist1−/− knockouts display cNCC phenotypes at E11.5, including abnormally compacted cell aggregations in the APC ectomesenchyme. Cell-lineage and marker analyses show that these aggregations are NCC-derived and robustly express Hand1 and Hand2 [14]. We hypothesized that these mutant phenotypes reflect aberrant NCC fate choice, and sought to better define these NCC aggregates.
To precisely examine Twist1 function during cNCC maturation, we conditionally inactivated Twist1 in NCCs at specific stages of Mus musculus (mouse) development using the Wnt1-Cre [15] and Hand1Cre [16] alleles, which respectively express Cre recombinase in pre-migratory and post-migratory cNCCs. Both cNCC-specific Twist1 ablation models display OFT defects; however, pre-migratory Twist1 deletion causes these defects with greater penetrance and severity, compared to post-migratory deletion. In contrast, the presence of NCC-derived nodules is evident in all Twist1 conditional knockouts (CKOs), regardless of the timing of gene ablation. Expression analyses show that Twist1 CKO nodules are molecularly similar to sympathetic ganglion neurons. We find that, unlike that of bona fide sympathetic ganglion neurons, ectopic neuron formation in Twist1 CKOs is independent of Hand2 function, indicating that these neurons are a distinct cell population. Similar to Hand1 and Hand2, Twist1 can molecularly interact with both the pro-neural Paired-like homeobox transcription factor Phox2b and HMG box transcription factor Sox10. Sox10 is upstream of Phox2b in the Bmp-dependent sympathetic neuron transcriptional program [17]. Here, we confirm that Sox10 regulation of Phox2b is direct. We demonstrate that Sox10 trans-activates the Phox2b promoter, and that Twist1 represses this transactivation. Twist1 itself can bind to an evolutionarily conserved non-canonical E-Box in the Phox2b promoter. Mutation of a C-terminal domain known as the Twist-box disrupts the ability of Twist1 to molecularly interact with Sox10, bind DNA, and transcriptionally repress Phox2b. Embryos harboring this Twist-box mutation (the Charlie Chaplin Twist1 allele) [18] similarly display ectopic neurons in their OFTs. Indeed, the appearance of these ectopic neurons is dependent upon Phox2b, as Phox2b ablation rescues ectopic neuron formation in Twist1 mutants. Finally, we show that ectopic Twist1 expression in NCCs, using a conditionally activatable CAG-CAT-Twist1 transgene activated by Wnt1-Cre, leads to sympathetic ganglia containing fewer neurons, in which Tyrosine Hydroxylase (TH), Phox2b, and Hand2 expression is diminished or absent, demonstrating that Twist1 expression is sufficient to disrupt normal neurogenic developmental programs. Together, these data suggest that Twist1 represses neuronal cell fate choice in the cNCC by repressing transcription of Phox2b, and reveal a fundamental mechanism controlling ectodermal versus mesodermal cell fate choice in NCCs.
Results
A subpopulation of NCCs in the Twist1 CKO cardiac OFT expresses neuronal markers
To assess Twist1 function during cNCC maturation, we conditionally inactivated Twist1 in pre-migratory NCCs using the Wnt1-Cre driver. Twist1 in situ hybridization of E10.5 embryos confirmed effective Wnt1-Cre-mediated NCC-specific gene deletion (Figure S1). Conditional ablation of Twist1 in pre-migratory NCCs produces abnormal cellular aggregates, indistinguishable from those observed in systemic Twist1 knockouts [14], in the APCs of the cardiac OFT. Lineage trace analyses using the ROSA26R reporter allele confirms that these nodules are NCC-derived (data not shown) and establishes a cell-autonomous requirement for Twist1 in developing cNCCs. At mid-gestation (E11.5), normal NCCs in the APCs generate extracellular matrix (ECM) that can be visualized by Alcian Blue staining (Figure 1A). The cNCC aggregations observed in Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKO embryos are devoid of ECM (arrowheads, Figure 1B). In situ hybridization analysis demonstrates that expression of Sox9, a transcriptional regulator of ECM components, is abnormally absent from the aggregations (arrowheads, Figure 1D), but is expressed normally within non-phenotypic cNCCs. In addition to Sox9, PlexinA2, Smad6, Hey2 and Pdgfrα, which are normally expressed in APC mesenchyme, are also excluded from the NCC aggregates (Figure S2). Thus, the cNCC aggregates in the cardiac OFT are molecularly distinct from the phenotypically normal cNCCs fated to differentiate along a mesodermal lineage and to ultimately contribute to the AoPS and valves. As reported previously, the feature that distinguishes these cNCC aggregates from normal cNCC mesenchyme is the expression of Hand1 and Hand2, which accounts for approximately 30–40% of the cNCC within the E11.5 OFT [14]. Indeed, neither Hand1 nor Hand2 expression is readily detectible within non-aggregated cNCCs in Twist1−/− embryos [14].
Fig. 1. Abnormal NCCs in Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKOs express neuronal, not mesenchymal, markers. 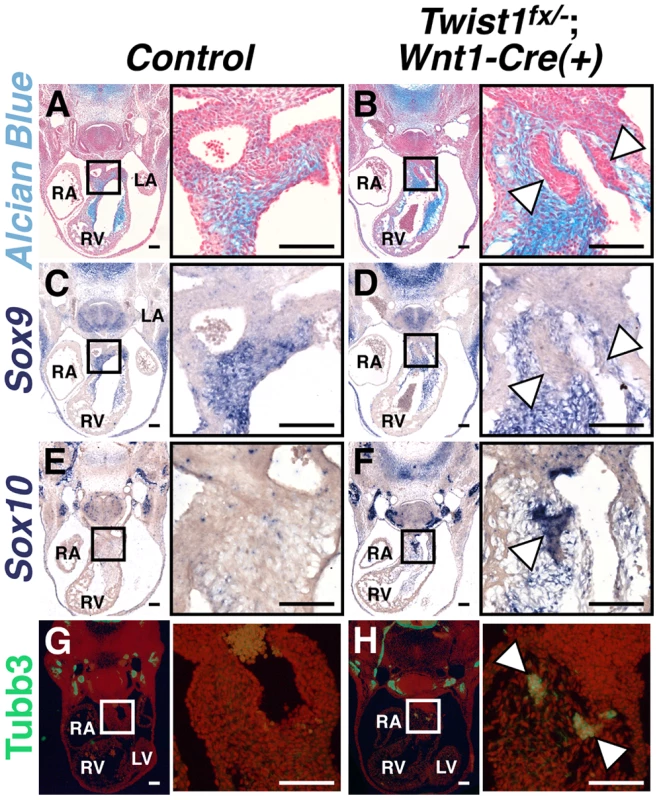
A, B) Alcian blue staining to visualize ECM reveals that the cNCC-derived nodules (B, arrowheads) in E11.5 Twist1fx/−;Wnt1-Cre(+) mutants are devoid of ECM. C, D) Sox9, a transcriptional regulator of ECM components, is also absent from the nodules (D, arrowheads). E–H) Cell aggregates express the neuronal precursor marker Sox10 (F, arrowheads) and neuronal marker Tubb3 (H, arrowheads). For all figures: LA, left atrium; LV, left ventricle; RA, right atrium; RV, right ventricle. Scale bars = 100 µm. As the NCC aggregations do not express the expected ecto-mesenchymal markers, we assessed the expression of genes associated with other NCC cell fates. The Bmp-dependent gene Sox10 is expressed in NCC-derived neuronal progenitors [12]. In situ hybridization analysis demonstrates that Sox10 mRNA is not detected in the APCs of control embryos; however, it is expressed in the Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKO aggregates (Figure 1F). Immunohistochemical analyses revealed that these aggregates also express the pan-neuronal marker Tubulin β-III (Tubb3), confirming their identity as ectopic neurons (Figure 1H).
Ectopic neurons in the Twist1 CKO OFT express sympathetic nervous system markers
As NCCs contribute to a number of distinct neuronal populations, we sought to determine the cellular identity of the ectopic neurons in the Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKO OFTs. Our previous data showed that Hand1 and Hand2, both markers of cardiac NCCs, are readily detectable in the OFT aggregates of Twist1−/− mutant embryos [14]. We confirmed this finding in Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKOs (Figure 2B, 2D). Importantly, Hand1 and Hand2 are only robustly co-expressed in NCC-derived sympathetic ganglion neurons (SGNs), and no other neuronal cell type [9], [19], [20]. We therefore hypothesized that these ectopic neurons may express other SGN markers. In situ hybridization revealed that NCC aggregates express transcriptional regulators of sympathetic neurogenesis, including the transcription factors Phox2a (data not shown) and Phox2b [21] (Figure 2F), the bHLH transcription factor Ascl1 [22] (Figure 2H) and the zinc finger transcription factor Gata3 [23] (Figure 2J). These cells also express the norepinephrine biosynthetic enzymes Tyrosine Hydroxylase (TH; Figure 2L) and Dopamine β Hydroxylase (DBH; Figure 2N) indicating that, like SGNs, these neurons are noradrenergic. Ectopic Phox2b - and Ascl1-positive NCCs are detectable in the Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKO pharyngeal arches as early as E10.5, and persist at least until E16.5 (Figure S3).
Fig. 2. Ectopic neurons in Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKO APCs express sympathetic neuron markers. 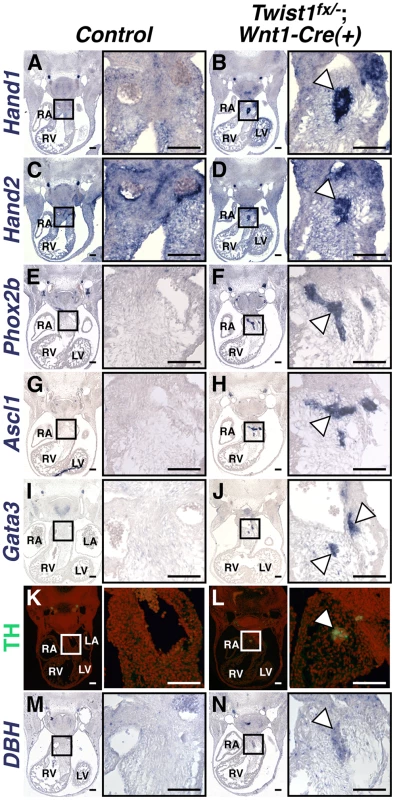
In situ hybridization shows that, in Control E11.5 embryos, Hand1 (A) and Hand2 (C) expression is detectable throughout the cNCC-derived APCs, where as expression of other components of the sympathetic neurogenesis pathway, including Phox2b (E), Ascl1 (G), Gata3 (I), TH (K, as assessed via immunohistochemistry), and DBH (M) are not detectable in this tissue. E11.5 Twist1fx/−;Wnt1-Cre(+) mutants, aggregates (arrowheads) express the transcription factors Hand1 (B), Hand2 (D), Phox2b (F), Ascl1 (H), and Gata3 (J), and the norepinephrine biosynthetic enzymes TH (L), and DBH (N). (n = 3). To further confirm that these neurons most resemble sympathetic neurons, we assessed a panel of sensory neuron markers, including TrkA, Brn3a, NeuroD1, and Runx1. We found that ectopic OFT neurons do not express these sensory neuron markers (Figure S4).
We also sought to distinguish these ectopic neurons, which are noradrenergic, from parasympathetic neurons, which are predominantly cholinergic. We therefore analyzed the cholinergic neuron markers Ret, VaCHT, and ChAT. Ret and VaCHT are expressed in both parasympathetic neurons, and in sympathetic neurons during their early development [24], and both are detectable in ectopic OFT neurons (Figure S4). Conversely, the parasympathetic-specific marker ChAT is not detectable above background levels in ectopic OFT neurons (Figure S4). Given that Hand1 and Hand2 are not expressed within parasympathetic neurons [25], [26], we conclude that the ectopic neurons in the Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKO APCs are most molecularly similar to sympathetic neurons.
In addition to the formation of ectopic OFT sympathetic-like neurons, Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKOs also display completely penetrant persistent truncus arteriosus (PTA; Figure S5G, S5K; Table S1). These structural OFT defects are presaged by the complete absence of detectable Semaphorin 3c (Sema3c) expression in Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKO cNCCs (Figure S6). Sema3c is required for septation of the OFT [27], [28] and may be directly regulated by Twist1 [29]. As PTA can result from either defective cell migration or NCC differentiation, a breakdown of either of these two mechanisms could cause the ectopic sympathetic-like neurons in the Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKO APCs. To distinguish between these two possibilities, we deleted Twist1 in post-migratory cNCCs.
Twist1 functions in post-migratory cNCCs to repress neurogenesis
NCC fate choice is largely determined by axial level of origin [2], [4], [10]. Twist1 is expressed in NCCs immediately following delamination from the neural tube and throughout subsequent migration. Loss of Twist1 disrupts cranial NCC migratory pathways [30]. To test whether loss of Twist1 either causes presumptive neural progenitor NCCs to similarly mis-migrate into the APC mesenchyme or alters cNCC fate choice, we examined Twist1 function during post-migratory cNCC maturation. To this end, we conditionally inactivated Twist1 using the Hand1Cre knock-in allele [16], which expresses Cre recombinase in post-migratory NCCs (Figure S5C, S6D). Twist1;Hand1Cre CKOs show a markedly reduced penetrance of PTA (Figure S5L, S5M; Table S1). This suggests that, for the OFT to septate properly, Twist1 function is required to regulate cNCC migration to the OFT during early development.
In contrast, the formation of ectopic neurons in E11.5 Twist1;Hand1Cre CKO OFTs occurs with 100% penetrance (Figure 3B and 3D, arrowheads). In situ hybridization and immunohistochemical analyses show that ectopic neurons express Sox10, Tubb3 (data not shown), TH (Figure 3B) and Ascl1 (Figure 3D). Thus, when Twist1 function is ablated in Hand1-lineage cNCCs that have completed migration, a subset of these cells then differentiate into neurons. These data indicate that ectopic neurons form in Twist1 mutant embryos via a novel post-axial specification mechanism whereby post-migratory cNCCs trans-differentiate. Additionally, although Sema3c expression was also disrupted in a majority of Twist1;Hand1Cre CKO OFTs (n = 3/4), unlike Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKOs, the penetrance was not 100%. Indeed, Sema3c expression was unaffected, even when ectopic Ascl1-positive cells were detectable (Figure S6). Collectively, these data demonstrate that OFT septation and repression of cNCC trans-differentiation are distinct Twist1-associated phenotypes, and that this Hand1-lineage-resticted trans-differentiation does not preclude the remaining cNCCs from maintaining characteristic cNCC gene expression (Figure S2) and differentiating normally once they arrive within the OFT.
Fig. 3. Ectopic sympathetic-like neurons are detectable in Twist1;Hand1eGFPCre CKO APCs. 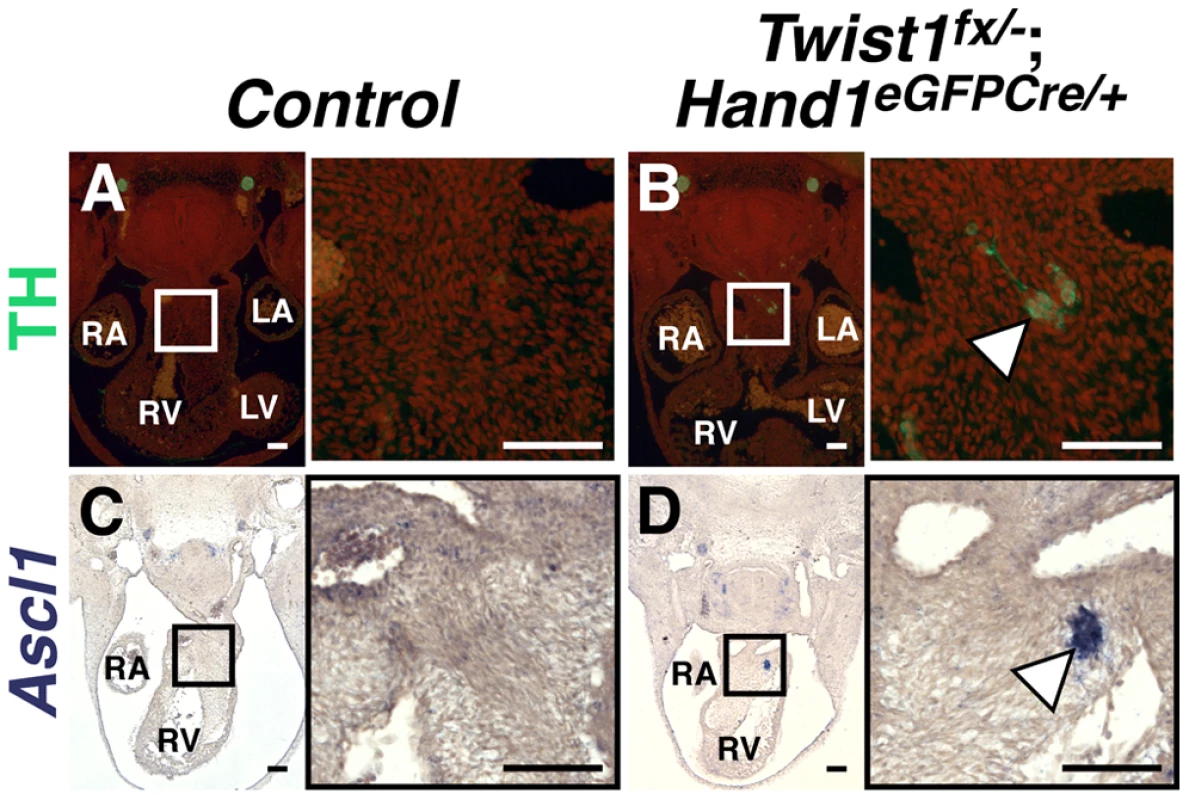
E11.5 Twist1fx/−;Hand1Cre mutant aggregates (arrowheads) express TH (B; n = 2) and Ascl1 (D; n = 4), whereas these factors are not detectable in Control APCs (A and C, respectively). A non-canonical pathway specifies ectopic sympathetic-like neurons in the Twist1 CKO OFT
To identify the transcriptional effectors of sympathetic neurogenesis that Twist1 regulates, we first explored genetic interactions with the related bHLH factor Hand2. Sympathetic neurogenesis depends upon Hand2 function [26], [31], [32]. As Twist1 and Hand2 are functionally antagonistic in the developing limb [33] we investigated a similar mechanism in the OFT. As expected, at E11.5, NCC-specific Hand2 ablation results in fewer DBH-positive neurons (compare Figure 4A1 and 4C1), reduced TH expression (data not shown), and complete loss of Hand1 expression (compare Figure 4E1 with 4G1) in the forming SGNs. Twist1;Hand2 double CKOs display similarly reduced SGN specification (Figure 4D1 and 4H1). Surprisingly, ectopic sympathetic-like neurons persist in the OFTs of E11.5 Twist1;Hand2 double CKOs (Figure 4D and 4H). These ectopic neurons robustly express TH (data not shown), DBH (Figure 4D2), and Hand1 (Figure 4H2). Endogenous Hand1 SGN expression is directly dependent upon Hand2 function [26], [32], [34]. Although the ectopic neurons in the Twist1 CKO APCs are molecularly similar to SGNs, their specification and expression of SG-specific markers is Hand2-independent, thereby distinguishing them as a separate neuronal cell population. Thus, Twist1 antagonism of Hand2 does not repress ectopic neurogenesis in developing cNCCs.
Fig. 4. Ectopic sympathetic-like neurons in Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKO APCs are not bona fide sympathetic neurons. 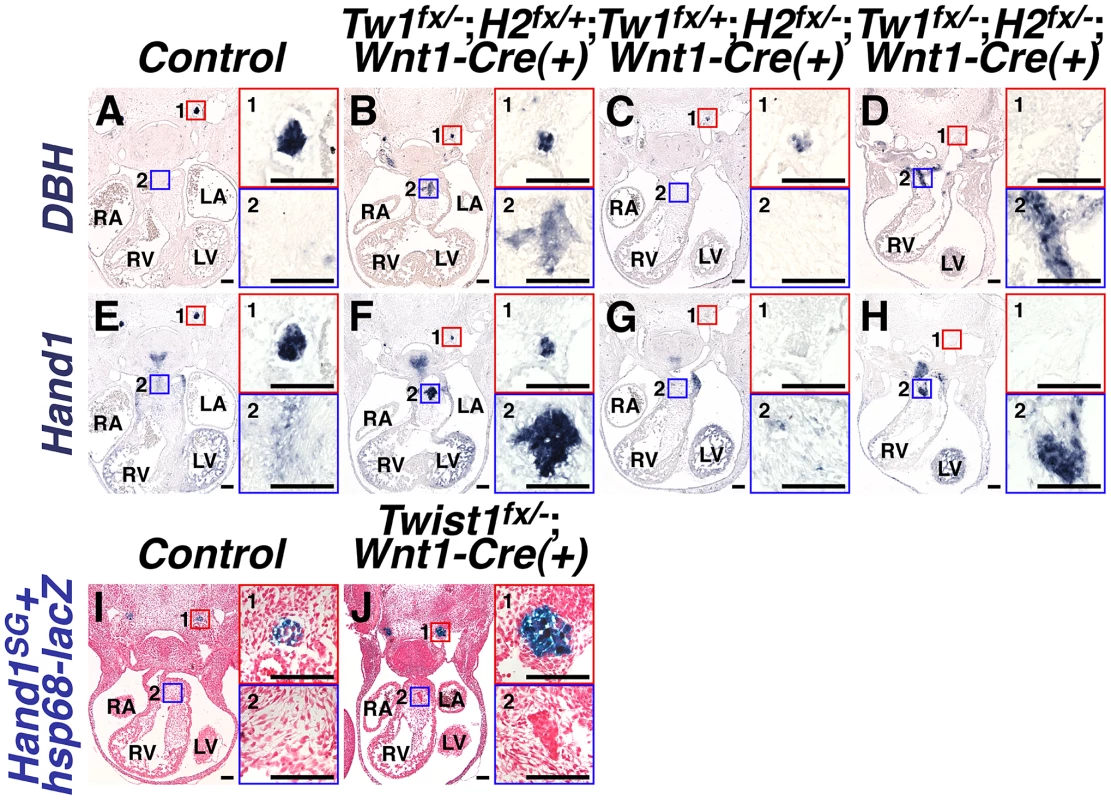
A–H) At E11.5, NCC-specific Hand2 ablation causes reduced DBH expression (compare inset 1 in A and C), and loss of Hand1 expression (compare inset 1 in E and G). However, in E11.5 Twist1fx/−;Hand2fx/−;Wnt1-Cre(+) mutants, robust ectopic sympathetic-like neurons persist and express comparatively high levels of DBH (inset D2; n = 4) and Hand1 (inset H2; n = 4). I, J) A Hand2-dependent cis-regulatory element proximal to Hand1 is sufficient to drive reporter transgene (Hand1SG+hsp68-lacZ) expression in developing SGNs at E11.5 (inset 1 in I and J). However, reporter transgene expression is not detectable in the ectopic neurons in the Twist1fx/−;Wnt1-Cre(+) CKO APCs (J2), indicating that this tissue-specific cis-regulatory element is not active in these cells (n = 4). We have identified a Hand2-dependent Hand1 cis-regulatory enhancer sufficient to drive reporter gene expression in the developing and adult SGNs [34]. To validate that the ectopic neurogenesis in Twist1 CKO APC mesenchyme is truly via a non-canonical mechanism, we assessed the expression of this SGN-specific enhancer (Hand1SG+hsp68-lacZ) on a Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKO background. Although this SGN-specific reporter transgene is normally expressed by the endogenous E11.5 SGNs of both control and Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKO embryos (Figure 4, 4I1 and 4J1), the Hand1 SGN-specific enhancer is not transcriptionally active in Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKO ectopic neurons, despite the presence of its direct regulators, Hand2 and Phox2b [34] Figure 4J2). Thus, although the ectopic neurons in Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKO APCs express Hand1 (Figure 2B; Figure 4F2; [14], this expression is driven by a Hand2-independent enhancer distinct from the one that drives SGN-specific expression. Thus, the molecular pathways regulating gene expression in the ectopic neurons of Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKO APCs are distinct from those endogenously regulating sympathetic neurogenesis.
Interestingly, Hand2-independent Hand1 expression in the Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKO ectopic OFT neurons suggests that Hand1 could be functionally redundant with Hand2, and that loss-of-function of both Hand1 and Hand2 would “rescue” the ectopic neurons in Twist1;Wnt1-Cre CKOs. To test this, we generated Twist1fx/−;Hand1fx/−;Hand2fx/−;Wnt1-Cre(+) triple CKOs (Figure S7). Triple CKO embryos were rarely viable past E10.5. Nevertheless, histological analysis clearly shows ectopic OFT neurons, further confirming that, although the 30–40% of cNCC undergoing neuronal trans-differentiation are marked by Hand1 and Hand2 [14], this aberrant NCC cell fate trans-differentiation caused by Twist1 loss-of-function is completely Hand factor independent.
Twist1 molecularly interacts with both Phox2b and Sox10 through a protein domain required to repress ectopic neurogenesis in the OFT
As Hand factors are dispensable for ectopic neuron formation in the Twist1 CKO APCs, we sought an alternative pro-neural factor(s) with which Twist1 interacts to repress neurogenesis. Hand2 and Phox2 proteins molecularly interact to synergistically affect critical transcriptional programs during sympathetic neurogenesis [26], [31], [32], [35]. Phox2b is molecularly upstream of Hand2, and these two factors auto-regulate each other via a feed-forward mechanism [21], [22], [36]. As Twist1 and Hand2 are closely related, we used co-immunoprecipitation to test for a possible interaction between Twist1 and Phox2b. Similar to Hand2, Twist1 molecularly interacts with Phox2b (Figure S8A and S8B). Twist1 molecularly interacts with both Runx2 [18] and Runx3 [36] through its carboxy-terminal Twist-box domain. Mutation of the Twist-box (S192P) impairs Runx molecular interactions. [18] Co-immunoprecipitation analyses using epitope-tagged Twist1 S192P showed that protein interactions between Twist1 and Phox2b are, in part, dependent upon the Twist-box domain (Figure S8A and S8B). However, transactivation assays in HeLa cells revealed that Twist1 does not significantly inhibit Phox2b auto-regulation, and thus did not provide compelling evidence that Twist1-mediated antagonism of neurogenesis is mediated though direct inhibition of Phox2b protein function. We therefore sought additional pro-neural factors with which Twist1 might interact.
Phox2b is not normally expressed in wild-type APCs (Figure 2E). Its presence in the APCs of Twist1 mutant embryos suggests that Twist1 could either directly repress Phox2b expression or repress the activity of a key Phox2b transcriptional regulator. Recently, Twist1 was shown to interact with and repress the function of the transcription factor Sox9 [37]. The related factor Sox10 functions directly upstream of Phox2b in the Bmp-dependent pathway that drives sympathetic neurogenesis [17]. To assess whether Twist1 can also interact with Sox10 and potentially inhibit its transcriptional activity, we performed co-immunoprecipitation assays. Twist1 molecularly interacts with Sox10, and although Twist1 S192P displays a comparatively reduced interaction with Sox10 (Figure 5A, 5B, asterisk, 48.3%+/−5.1%, p-value = 0.002), Twist1 T125;S127A, a Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome-associated Helix I dimerization mutant, does not (Figure 5A, 5B, 102.7%+/−12.0%, p-value = 0.85). Thus, as has been reported for Sox9 [37], Sox10 also interacts with Twist1 in a Twist-box dependent manner.
Fig. 5. The Twist-box domain of Twist1 is required for molecular interaction with Sox10 and for Twist1 binding to the Phox2b promoter. 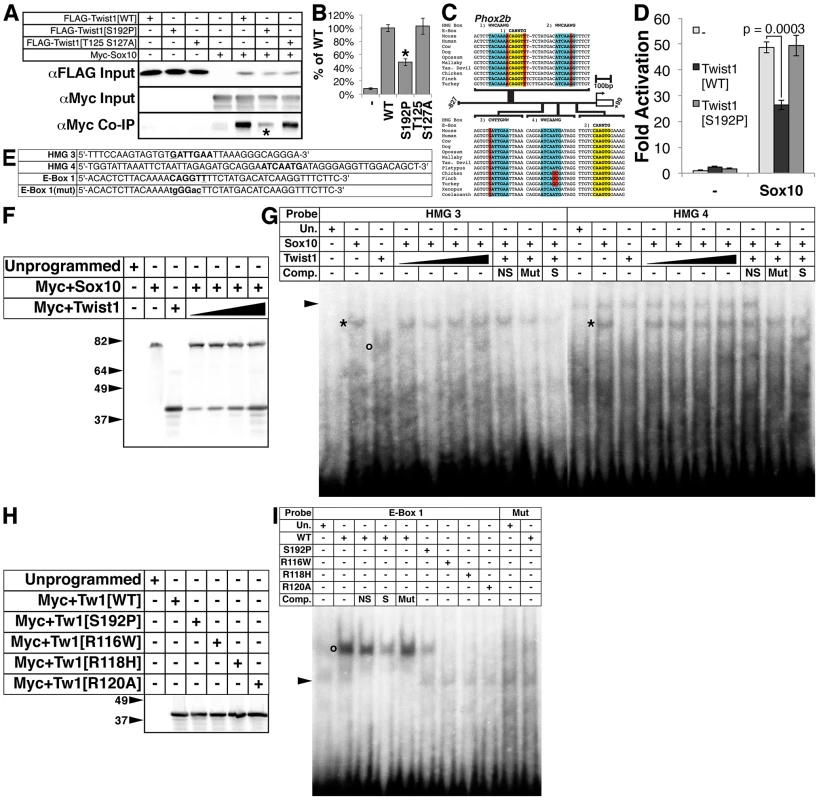
A) Co-immunoprecipitation assays (n = 3) using epitope-tagged variants of Twist1 and Sox10 show that Twist1 molecularly interacts with Sox10. This interaction is diminished in the Twist1 S192P mutant (asterisk), but not the Twist1 T125;S127A mutant. B) Densitometry analyses quantitate these results. C) Bioinformatic analyses uncovered four evolutionarily conserved HMG Box binding sites (highlighted in blue) and two conserved E-Box binding sites (highlighted in yellow) within in the 827 bps 5′ to the Phox2b transcription start site. Nucleotides that diverge from established consensus sequences are highlighted in red. D) Transactivation assays of the Phox2b promoter show that Sox10 upregulates gene expression from the Phox2b promoter 48.9+/−2.2-fold. Transcriptional upregulation is significantly reduced to 26.3+/−1.9-fold (p-value = 0.0003) when Sox10 is co-transfected with Twist1. When Sox10 is co-transfected with the Twist1 S192P mutant, Twist1 repression of Sox10 activity on the Phox2b promoter is lost (49.3+/−3.9-fold; p-value = 0.92). E–I) Both (E) radiolabeled oligonucleotides containing HMG Box or E-Box consensus sites (bold) and (F) reticulocyte lysates programmed with Myc+Sox10 and/or Myc+Twist1 were used to confirm that (G) Sox10 directly binds to cis-elements within the Phox2b promoter (asterisks), and that Twist1 has no appreciable effect upon Sox10 DNA binding. An open circle denotes a complex formed between HMG 3 and Twist1. H) A Western blot for α-Myc verifies that the Myc-tagged Twist1 variants transcribed in vitro were synthesized in equivalent amounts. I) EMSAs employing these lysates revealed that E-Box 1 is bound robustly by wild-type Twist1 (open circle), weakly by Twist1 S192P, and not at all by Twist1 R116W, Twist1 R118H, or Twist1 R120A. Mutation of the E-Box, E-Box 1(Mut), completely ablated Twist1 binding. Underlined nucleotides in oligo sequences indicate those that diverge from established consensus sequences. Mutated nucleotides are in lower case. Arrowheads in EMSAs denote non-specific binding. NS, non-specific unlabeled competitor; Mut, mutant unlabeled competitor; S, specific unlabeled competitor. Sox proteins bind the consensus sequence WWCAAWG [38]. Bioinformatic analyses revealed putative HMG box cis-elements in the Phox2b 5′ promoter that are evolutionarily conserved (Figure 5C, highlighted in blue). Sox10 is required for Phox2b expression in vivo [17]. Given the presence of evolutionarily conserved putative Sox10 cis-elements in the Phox2b promoter (Figure 5C), we tested whether Sox10 might transactivate Phox2b directly. Indeed, Sox10 significantly upregulates gene expression from the Phox2b promoter by 48.9+/−2.2-fold (Figure 5D, p-value = 0.0002). Co-expression of Twist1 inhibits Sox10-mediaded transactivation, reducing its transcriptional activation to 26.3+/−1.9-fold (Figure 5D, p-value = 0.0003). Co-expression of Twist1 S192P significantly ameliorates this Sox10 inhibition, restoring Sox10 transactivation to 49.3+/−3.9-fold (Figure 5D, p-value = 0.92). Together, these data indicate that Twist1 molecularly interacts with Sox10 through its Twist-box domain, and partially represses trans-activation of the Phox2b promoter.
Twist1, through its Twist-box domain, inhibits DNA binding of both Runx2 [18] and Sox9 [37]. We therefore reasoned that Twist1 might similarly inhibit Sox10 binding to the Phox2b promoter. We therefore first confirmed Sox10 DNA binding to the conserved HMG boxes in the Phox2b 5′ promoter through electrophoretic mobility assays (EMSA) using radiolabeled oligonucleotides (Figure 5E) and in vitro translated Myc-tagged Sox10 (Figure 5F). Sox10 binds to the proximal two HMG boxes, termed HMG 3 and HMG 4 (Figure 5G, asterisks), but not the distal two HMG boxes, termed HMG 1 and HMG 2 (data not shown). We conclude that Sox10 can bind to conserved HMG boxes in the Phox2b promoter, supporting that Sox10 directly regulates Phox2b expression. We then synthesized in vitro translated Myc-tagged Sox10 in the presence of increasing amounts of Myc-tagged Twist1 (Figure 5F). EMSAs revealed that Twist1 does not disrupt Sox10 DNA binding to HMG 3 and HMG 4 (Figure 5G, asterisks). However, Twist1 does bind within HMG 3 to a non-canonical cis-element (Figure 5G, open circle). Given this surprising result, we then tested whether Twist1 can bind directly to other elements within the Phox2b promoter.
Twist1 binds to consensus sites termed E-Boxes (CANNTG) [39], [40]. Bioinformatic analyses uncovered one conserved E-Box and one conserved E-Box-like element within the Phox2b 5′ promoter (Figure 5C, highlighted in yellow). We in vitro translated Twist1 and Twist1 S192P protein (Figure 5H) to assess Twist1 DNA binding to these E-Boxes. As controls, we included three mutant forms of Twist1 in which conserved arginines in the basic domain have been mutated (Figure 5H). Of these three mutants, Twist1 R116W [41], Twist1 R118H [42], and Twist1 R120A [43], the former two are associated with the congenital disorder Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome, and all are predicted to have impaired DNA binding capabilities [44]. Although Twist1 displayed no binding to the perfect consensus E-Box 2 (data not shown), it robustly bound to the non-canonical E-Box 1 (Figure 5I, open circle). Twist1 did not detectably bind to a mutated (mut) E-Box 1 oligo (Figure 5I), in which the E-Box core was disrupted (Figure 5I). As predicted, none of the Twist1 basic domain mutants bound to E-Box 1. Twist1 S192P does bind to E-Box 1; however, it binds more weakly when compared to WT Twist1. Given that equivalent amounts of Twist1 and Twist1 S192P were added to each EMSA, the strength of DNA-binding is quantitative (see [39]; Figure 5H and 5I). Together, these data suggest that the Twist-box is critical not only for Twist1 protein interactions with Sox10, but also for Twist1 DNA binding. Thus, Twist1 inhibition of Phox2b transcription is likely mediated through direct DNA binding of non-canonical, conserved E-Box elements in the Phox2b promoter. Moreover, Twist1 could directly interact with the potent Phox2b trans-activator Sox10 while both factors are bound to the promoter.
As Phox2b is considered a master regulator of autonomic neurogenesis, [9] we hypothesized that disruption of the Twist-box in vivo would lead to aberrant Phox2b activation, and, consequently, the appearance of ectopic neurons in the developing OFT similar to those observed in Twist1 CKO embryos. The Charlie Chaplin Twist1 allele (Twist1CC) is a Twist1 S192P point mutation that specifically disrupts function of the Twist1 Twist-box domain. Embryos harboring this mutant allele exhibit craniofacial and limb abnormalities [18]. To test the hypothesis that Twist1-mediated repression of Phox2b is necessary to repress ectopic neurogenesis in the developing OFT, we examined the OFT phenotypes of both heterozygous and homozygous Twist1CC embryos. Twist1CC/CC mutants lack overt structural OFT phenotypes (Figure S5I, S5M). Indeed, Sema3c expression is not disrupted in either Twist1CC/+ or Twist1CC/CC mutants (Figure S6F, S6G). These data suggest that the Twist-box is dispensable for proper cNCC migration and OFT morphogenesis. However, as predicted by the necessity of the Twist-box for robust Sox10 interactions and binding to the Phox2b promoter, ectopic OFT neurons are detectable in the APCs of both Twist1CC/CC homozygous mutants and Twist1CC/+ heterozygotes. In Twist1CC/+ heterozygous embryos, dispersed Phox2b - (Figure 6B) and Ascl1-positive (data not shown) cells are detectable in the APC ectomesenchyme. Relatively few of these cells are TH-positive, however, suggesting that these ectopic cells fail to undergo complete neuronal differentiation (Figure 6E, arrowhead). Twist1CC/CC homozygous mutants display more robust ectopic ganglia that are positive for Phox2b (Figure 6C), Ascl1 (Figure 7A), and TH (Figure 6F). Collectively, these data show that Twist1 interacts with Sox10 and Phox2b at least partially via its Twist-box domain, and that this domain is required to inhibit cNCC trans-differentiation into ectopic sympathetic-like neurons.
Fig. 6. The Twist-box domain of Twist1 is required for repression of ectopic neurogenesis. 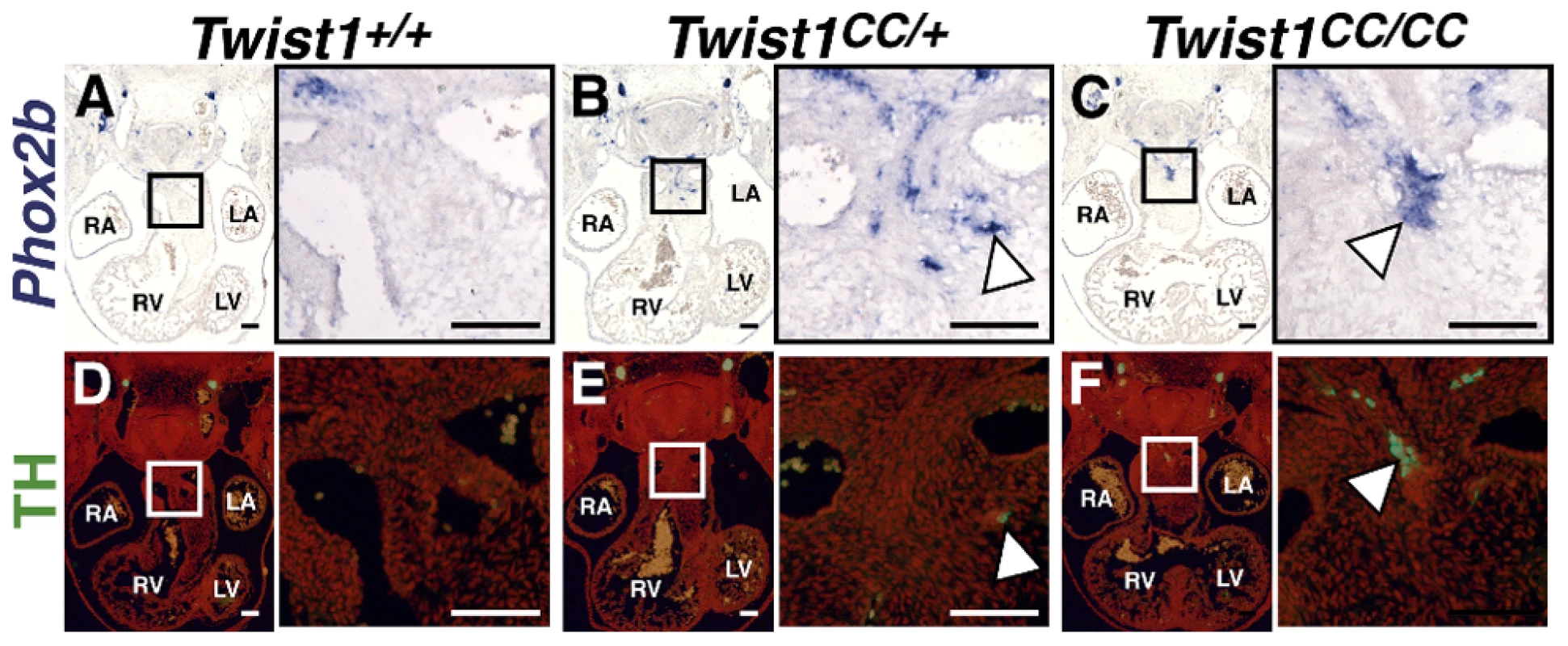
Analyses of Twist1CC mutant embryos that harbor this Twist box mutation, reveal that Twist1CC/+ heterozygous OFTs contain dispersed or relatively small aggregates of Phox2b-positive cells (B) and rare TH-positive cells (E, arrowhead) Twist1CC/CC embryos contain robust ectopic Phox2b-positive ganglia (C) and a greater number of TH-positive neurons (F, arrowhead). Neither Phox2b- nor TH-positive cells are detectable in Twist1+/+ APCs (A and D, respectively). Fig. 7. Ectopic neurogenesis in Twist1CC mutants is Phox2b-dependent. 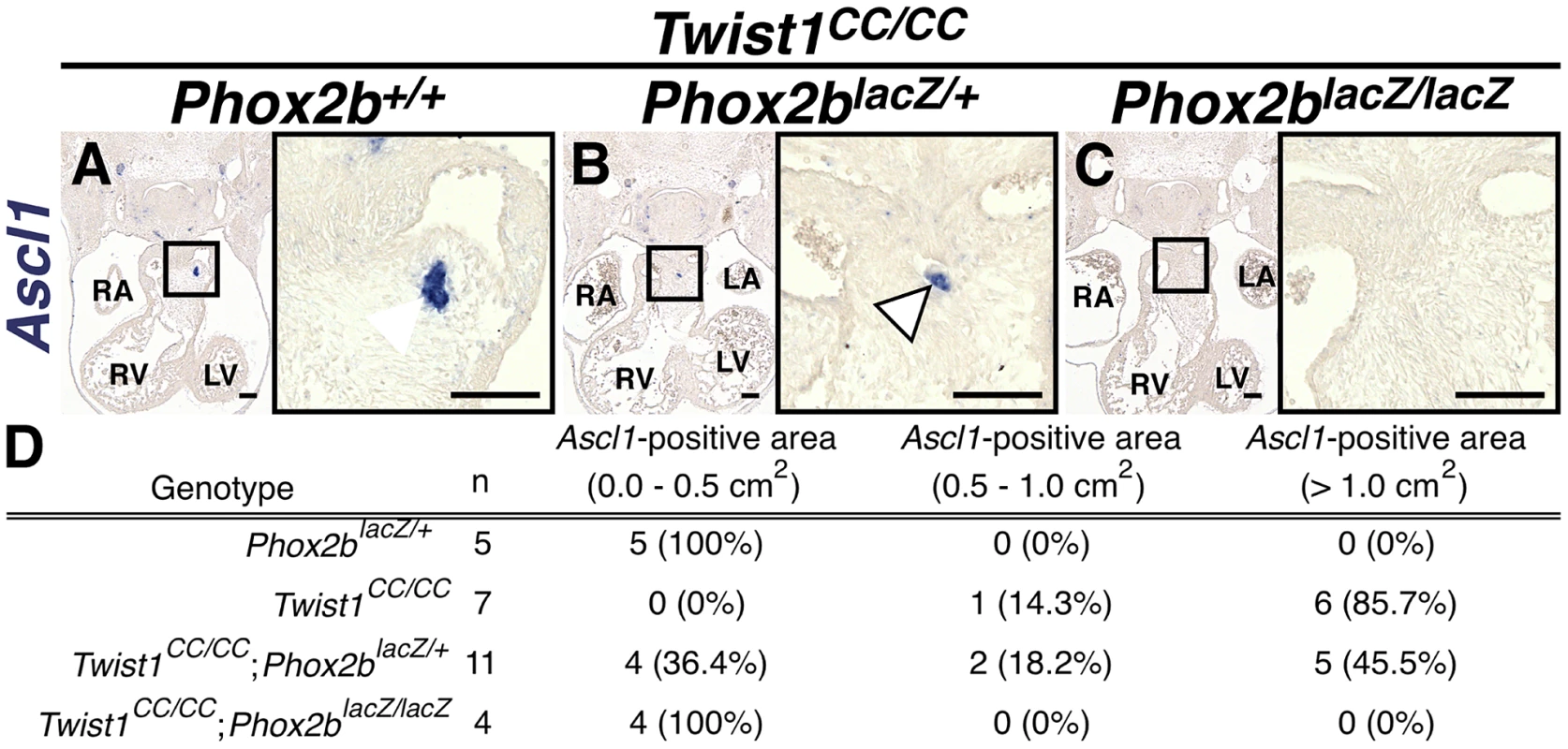
A) All Twist1CC/CC homozygous OFTs examined contain robust aggregates of Ascl1-positive cells. B) Concurrent Phox2blacz/+ haploinsufficiency tended to reduce the size of these aggregates (arrowhead). C) No Ascl1-positive cells were evident in Twist1CC/CC;Phox2blacz/lacZ OFTs. D) Morphometric quantification of these analyses validated these results. Ectopic neurogenesis in Twist1 mutants is Phox2b-dependent
To confirm that Phox2b upregulation is absolutely required to modulate post-migratory NCC cell fate choice in Twist1 mutants, we assessed ectopic neurogenesis in E11.5 Twist1;Phox2b doubly mutant embryos. Robust ectopic aggregates of Ascl1-expressing cells were evident in Twist1CC/CC homozygous mutants (Figure 7A). Interestingly, the size of these aggregates appeared reduced when Phox2b gene dosage was attenuated to heterozygosity (Figure 7B). It is not technically possible to count individual staining-positive cells following in situ hybridization. We therefore validated our results using morphometric analyses. Quantification of the Ascl1 staining-positive area in each sequential section of these mutant embryos revealed that, while a reduction of Phox2b gene dosage had no appreciable effect on Ascl1 staining in 5 out of 11 Twist1CC/CC;Phox2blacZ/+ mutants examined, 4 out of 11 of these mutants showed reduced ectopic Ascl1 staining comparable to that seen in control (Phox2blacZ/+) APCs (Figure 7D). Ectopic neurons were not detectable in either Twist1CC/+ or Twist1CC/CC mutants when Phox2b function was completely ablated (Figure 7C, data not shown). Collectively, these results validate the hypothesis that Twist1 ultimately represses the proneural activity of Phox2b in NCCs by inhibiting its transcription both via direct molecular antagonism of Sox10 activity and through binding to the Phox2b promoter. These findings provide the first evidence, to our knowledge, that the potential ectodermal and mesodermal cell fates of post-migratory NCCs can be regulated through functional antagonism between transcription factors.
Ectopic expression of Twist1 disrupts sympathetic neurogenesis
If Twist1 is a true repressor of ectodermal cell fate, then ectopic expression of Twist1 in NCCs should inhibit differentiation of endogenous SGNs. To test whether Twist1 can repress sympathetic neurogenesis, we used a conditionally activatable transgene (CAG-CAT-MycTwist1) [40] to ectopically express Twist1 in the NCC progenitors of SGNs. TH expression, as revealed through immunohistochemistry of E12.5 embryos, was either absent in thoracic sympathetic chain ganglia (Figure 8B), or was restricted to a few cells (Figure 8C). Co-localization of Twist1, visualized via a Myc epitope tag, and TH was not observed (Figure 8C). Tubb3 immunohistochemistry and Phox2b in situ hybridization analyses confirm that the thoracic sympathetic ganglia in CAG-CAT-MycTwist1(+);Wnt1-Cre(+) embryos are either absent (Figure 8E, 8K), or markedly reduced (Figure 8F, 8L). In the Control thoracic sympathetic chain, Sox10-expressing presumptive support cells surround the ganglia, which are mostly, but not entirely, Sox10-negative (Figure 8G). In E12.5 CAG-CAT-Twist1(+);Wnt1-Cre(+) transgenic embryos, the hypoplastic thoracic sympathetic chain ganglia are either entirely positive for Sox10 (Figure 8K, arrowhead) or display a markedly reduced core of Sox10-negative cells (Figure 8I, arrowhead). Hand2 mRNA expression is also drastically reduced in E12.5 CAG-CAT-Twist1(+);Wnt1-Cre(+) thoracic sympathetic chain ganglia, and is occasionally absent, even when neurons in adjacent sections express Phox2b, suggesting that normal SGN regulatory cascades are disrupted in Twist1 mis-expressing SGNs (Figure 8N, 8O). These findings, in combination with Twist1 loss-of-function and genetic interaction analyses, demonstrate that Twist1 is a potent repressor of sympathetic neurogenesis, and that Twist1 antagonizes downstream Bmp targets to act as a novel post-migratory cell fate switch in the NCCs that populate the cardiac OFT.
Fig. 8. Sympathetic neurogenesis is disrupted by Twist1 mis-expression. 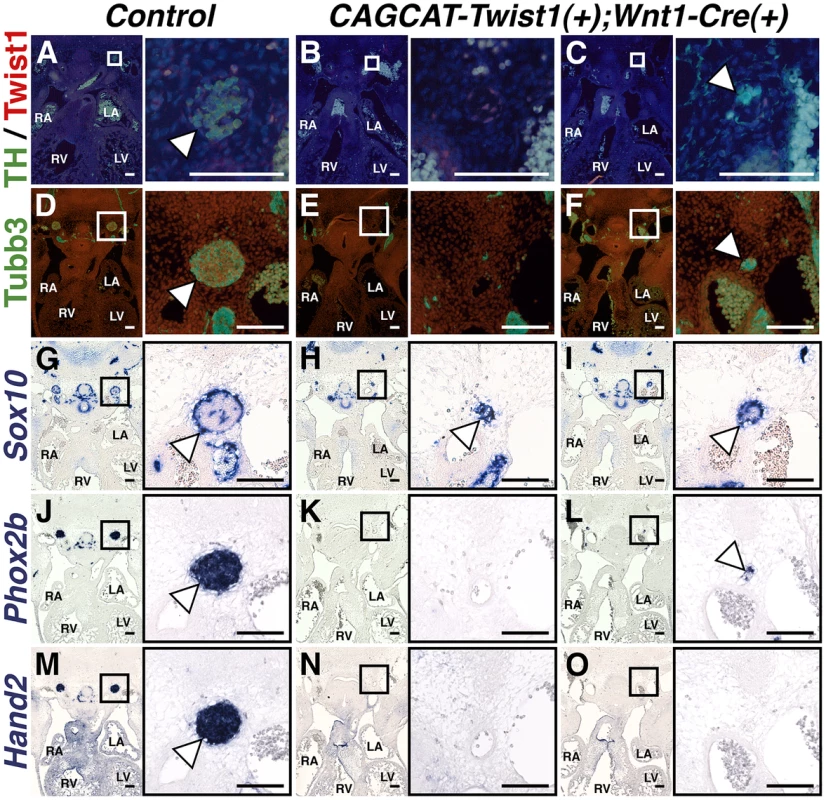
In E12.5 Control embryos, the thoracic sympathetic chain ganglia (arrowheads) express TH (A), Tubb3 (D), Phox2b (J), and Hand2 (M). Sox10-expressing support cells surround the thoracic sympathetic chain ganglia (G, arrowhead). In thoracic sympathetic chain ganglia in E12.5 CAGCCAT-Twist1(+);Wnt1-Cre(+) transgenic embryos, expression of TH, Tubb3, Phox2b, and Hand2 is either absent (B, E, K, and N), or markedly reduced (C, F, L, and O). In the latter instance, TH (green) and Twist1 (red) expression is largely mutually exclusive (n = 3). These hypoplastic thoracic sympathetic chain ganglia are either entirely positive for Sox10 (H, arrowhead) or display a markedly reduced core of Sox10-negative cells (I, arrowhead). Discussion
Here, we describe a novel cell fate switch that regulates post-migratory NCC differentiation to either an ectodermal or a mesodermal cell fate. The bHLH transcription factor Twist1 is expressed in migratory and post-migratory cNCCs, but is not expressed in the NCC-derived SGNs. Loss of Twist1 in Wnt1-Cre-expressing NCCs results not only in structural OFT defects, but also the formation of dense aggregates of sympathetic-like ganglia in the APCs of the cardiac OFT. These neurons express Sox10, Phox2b, Ascl1, Gata3, Hand1, Hand2, TH and DBH, which are all components of the BMP-induced SGN differentiation program, but not markers of sensory neurons or specific markers of parasympathetic neurons. Our earlier work shows that these ectopic neurons are marked by both Hand1 and Hand2 expression, and account for approximately 30–40% of E11.5 OFT cNCCs [14]. Deletion of Twist1 in the smaller, post-migratory Hand1Cre lineage-derived subpopulation of cNCCs reveals that this ectopic neurogenesis is a bona-fide cell fate trans-differentiation from a mesenchymal to neuronal cell type, and is not a consequence of the altered migration of trunk NCCs. The penetrance of OFT structural defects, such as PTA, is greatly reduced in embryos in which Twist1 is deleted using the Hand1Cre, indicating that NCC migration-dependent phenotypes are largely rescued in this model (Table S1). Thus, cells fated to contribute to the smooth muscle and valves of the OFT can be reprogrammed to an SGN-like fate in the absence of Twist1. Both Wnt1-Cre and Hand1Cre Twist1 CKOs survive until birth and, in some Hand1Cre Twist1 CKOs, exhibit no significant OFT defects other than ectopic neurons. Furthermore, although they have completely penetrant ectopic neurons, Twist1CC mutants do not display either structural OFT defects or diminished Sema3c expression. In conjunction with normal marker analysis (Figure S2), these data suggest that Twist1 function is solely required in specific subpopulations of cNCCs, and that unaffected cNCCs correctly follow their developmental programs in the absence of Twist1.
Mechanistically, Twist can physically interact with other proteins using both its bHLH and Twist-box domains [18], [37], [45], [46]. Twist1 antagonistically interacts with Hand2 [33]. Although loss of Hand2 in NCCs dramatically effects the development of the endogenous sympathetic chain, as previously reported [26], [32], the trans-differentiation of the SGN-like neurons in the OFT was not affected. Furthermore, Hand1 expression, which is directly dependent upon Hand2 function in SGNs [34], is maintained, but its expression is not mediated through its identified SGN-specific enhancer (Figure 4). Although we have demonstrated that the Hand1 SG-enhancer is not auto-regulated by Hand1 [34], we analyzed Twist1;Hand2;Hand1 triple CKO mice. Ectopic neurons remain histologically evident in these mutants, demonstrating that the trans-differentiation of cNCCs to an SGN-like fate is independent of Hand factors and, by consequence, represents a non-canonical transcriptional program. Hand factor expression, instead, appears to define which cNCCs convert to ectopic neurons, as opposed to those that retain their normal developmental programs.
Indeed, these studies raise questions concerning the developmental origin of neurons innervating the heart. Although it is known that the NCCs contribute neurons to the arterial pole of the heart [47]–[49], the origin of these neurons and the mechanisms regulating their development are poorly understood. The NCCs migrating to the arterial pole of the heart were thought to possess limited neurogenic potential [50]. Nonetheless, a subset of NCCs migrating to the caudal pharyngeal arches is thought to contribute to the cholinergic cardiac ganglia within the parasympathetic plexus [51]. These neurons are initially observed at E11.5, but are not consistently and robustly detectable until E12.5 [50]. We observe noradrenergic ganglia, identified through their expression of TH and DBH, in the APCs of Twist1 mutant embryos at E11.5. The presumptive NCC progenitors of these neurons, identified through Sox10, Phox2b, Ascl1, Hand2 and Hand1 expression, are evident in the E10.5 Wnt1-Cre CKO OFTs a day earlier, and in a much larger proportion of NCCs. It is notable that not all of the NCCs occupying the Twist1 mutant APCs trans-differentiate into neurons. As stated above, the only established distinguishing characteristic of this subpopulation of cells is that they express the two Hand genes, while the remaining, ostensibly unaffected cells do not (Figure 2B; [14]). The significance of this observation is not clear, as Hand factors are not required for the differentiation of these ectopic neurons. Furthermore, it is unclear whether this trans-differentiation constitutes a corruption of endogenous neuronal differentiation pathways, or whether within a specific subpopulation of NCCs migrating to the APCs, which are competent to differentiate into neurons, Twist1 functions to repress neurogenic pathways, preventing them from differentiating in such a manner. It would thus be of interest to further explore the differences inherent in NCCs competent to differentiate into neurons in the APCs, and those that are not.
The Twist-box domain of Twist1 interacts with Runx2, Runx3 and Sox9 [18], [37], [46]. These interactions repress the respective functions of these non-bHLH factors by interfering with their DNA binding [18], [37], [46]. Here, we show that Twist1 (via the Twist-box domain) can both interact with the potent trans-activator of Phox2b transcription Sox10 and inhibit transcriptional activation of the Phox2b promoter (Figure 5A–5D). This repression is not mediated through simple interference with Sox10 DNA-binding to the Phox2b promoter (Figure 5G). Rather, Twist1 itself can bind to conserved, non-canonical E-box elements within the Phox2b promoter in a manner that is Twist-box dependent (Figure 5I). This finding is the first evidence that Twist-box mutations can influence Twist1 DNA binding. Co-immunoprecipitation experiments indicate that the Twist1 S192P mutation does not compromise Twist1 homodimerization, (J. Vincentz and A. Firulli, unpublished results). This suggests that this impaired DNA binding is not the result of defective Twist1 dimerization, but may instead result from a conformational change to the Twist1 secondary structure that impairs juxtaposition of the two required basic DNA-binding domains within the Twist1 S192P homodimer. It should also be noted that the cis-element to which Twist1 binds does not conform to a typical E-box sequence. The sequence, CAGGTT, is a putative binding site for the zinc-finger transcriptional repressor Snai1 (Snail) [52]–[54]. Snai1 and Twist1 can genetically interact in Drosophila and mouse [55], [56]. Like Twist1, Snai1 and the related factor Snai2 (Slug) is a crucial regulator of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) [12]. Indeed, Snai1/Snai2, in the presence of Sox9, is sufficient to induce an EMT in neural epithelial cells [57]. Thus, functional interactions between both Twist1 and Snai1/Snai2 with Sox proteins during NCC development would be an intriguing avenue of further study.
Phox2b is both necessary and sufficient to drive the SGN cell fate program [22], and Phox2b activation is dependent upon Sox10 [17]. The Twist1CC mouse model shows that disruption of the Twist-box is sufficient to promote cNCC trans-differentiation. Normal cNCC fate choice is partially restored when Phox2b gene dosage is reduced to heterozygousity and completely rescued when Phox2b function is completely ablated, demonstrating its necessity to initiate SGN cell fate. Additionally, Twist1 can interact with the bHLH factor Ascl1, as determined via co-immunoprecipitation analysis (data not shown). Collectively, Twist1 then interacts with at least five of the key SGN cell fate transcriptional regulators (Figure S9). Given that both cNCC and SGN NCC transcriptional programs are initiated by Bmp-signaling, and that these two programs, at least in part, share key transcriptional regulators (Hand1, Hand2, Gata3; [58], Sox4 [59], and (likely) Sox11 [60], [61]), it is obvious that a switch to ensure that the correct cell fate is specified and maintained is built into these developmental programs. Twist1 is a strong candidate to fulfill such a role.
Indeed, when Twist1 is expressed throughout the Wnt1-Cre-expressing NCCs, we observe a reduction in the differentiation of SGNs as indicated by the mutual exclusivity of Myc-Twist1 and TH immunoreactivity, decreased expression of the pan-neuronal marker Tubb3 and loss of expression of both Hand2 and, more importantly, Phox2b. Additionally, the majority of the cells remaining in these hypoplastic ganglia express Sox10 (Figure 8H, 8I). We can draw two conclusions from this observation. First, the presence of these Sox10-positive cells, along with that of Myc-Twist1-positive cells (Figure 8B, 8C), confirms that NCC-derived progenitors retain the ability to migrate properly to the region proximal to the dorsal aorta when Twist1 is ectopically expressed. Second, as Sox10 is initially broadly expressed in NCC-derived neural precursors, but, by E12.5, is largely restricted to the surrounding support cells, we can infer either that ectopic Twist1 expression in NCCs specifically disrupts sympathetic neurogenesis, but not gliogenesis, or that Sox10 is not downregulated in Twist1-overexpressing NCC-derived neural precursors, and these cells therefore fail to differentiate. In either case, this data clearly demonstrates that ectopic Twist1 expression in neuronal precursor cells fundamentally impairs sympathetic neurogenesis, and potentially maintains these cells in a precursor state.
It is intriguing to speculate about the insight these findings may provide into the role of TWIST1 in cancer. Reactivation of TWIST1-regulated embryonic programs has been proposed to contribute to tumor progression [62]. TWIST1 induces EMT in tumor cells, and thus plays a dominant role in defining the metastatic potential of primary tumors [63]. In both embryonic and adult stem cells, Twist1 is also thought to prevent differentiation, thus promoting a stem cell-like phenotype [13]. Thus, Twist1 represents a single factor that can intimately link two cellular processes, EMT and maintenance of a stem cell-like fate, both integral to tumor cell progression. As our data demonstrates that Twist1 can functionally antagonize key regulators of a sympathetic neuronal identity, it would be of interest to closely examine the function of TWIST1 in neuroblastomas and other tumors affecting neuronal derivatives of NCCs. TWIST1 overexpression in N-Myc-amplified neuroblastomas has been shown to inhibit p53-dependent apoptosis [64]. Pheochromocytomas are neoplasms originating from NCC-derived adrenal chromaffin cells. Chromaffin cells have a molecular profile similar to that of SGNs. Like SGNs, chromaffin cells do not normally express Twist1. TWIST1 is frequently upregulated in pheochromocytomas and, intriguingly, this aberrant expression is tightly associated with malignancy in these tumors [65]. Thus, the model presented here, by which Twist1 represses neuronal cell identity in NCC derivatives, may ultimately shed light upon the role of TWIST1 in cancer.
Materials and Methods
Transgenic mice
Genotyping of the Twist1tm1Bhr (Twist1; [66]), Twist1tm2Bhr (Twist1fx; [67] provided by James Martin), Tg(Wnt1-cre)11Rth (Wnt1-Cre; [68]), Hand1tm1.1(EGFP/cre)Abfi (Hand1eGFPCre; [16]), Hand2tm1Cse, (Hand2fx; [32]), CAGCAT-Twist1; [40], Hand1SG-hsp68-lacZ; [34], Hand1tm2Eno (Hand1lx; [69] provided by Eric Olson) and Gt(ROSA)26Sortm1Sor (R26RlacZ; [70] alleles was performed as described. A 125bp region containing the mutated nucleotide in the Twist1Ska10 (Twist1CC; [18]) allele was amplified using the primers Twist1CC(F), 5′-ACGAGCTGGACTCCAAGATG-3′, and Twist1CC(R), 5′-GGAGCTCCGCTGCTAGTG-3′. Amplicons were then purified and sequenced. Phox2btm1Jbr (Phox2blacZ; [71] provided by Michelle Southard-Smith and Jean-FranÇois Brunet) mice and embryos were genotyped using the primers Phox2bEx2(F), 5′-GTTCAGTGGCCCTTCACATC-3′, Phox2bEx2(R), 5′-TCCTCTCACGGGACACTTCT-3′, and lacZ_5′_out, 5′-CGGAAACCAGGCAAAGCGCC-3′ to generate ∼500 bp WT and ∼250 bp mutant amplicons.
Histology
Alcian Blue, Nuclear Fast Red, Hematoxylin and Eosin (H&E) staining were performed as described [14], [72]. X-gal staining was performed as described [16].
In situ hybridization
1Section in situ hybridizations were performed on 10 µm paraffin sections as described [14], [72]. Antisense digoxygenin-labeled riboprobes were synthesized using T7, T3 or SP6 polymerases (Promega) and DIG-Labeling Mix (Roche) using the following plasmid templates: Twist1 (provided by Richard Behringer), Hand1, Hand2, Sema3c, Runx1, Hey2 (provided by Yasuhide Furuta), Sox9 (provided by Benoit De Crombrugghe), Sox10 (provided by Paul Trainor), Ascl1 (provided by Xin Zhang), Phox2b, VaCHT (provided by Peter Cserjesi), Gata3, Ret, DBH (provided by Jean-FranÇois Brunet), PlexinA2, Pdgfrα, Smad6 (provided by Jonathan Epstein), TrkA (provided by David Ginty), Brn3a, NeuroD1 (both provided by Eric Turner), and ChAT (IMAGE clone #8734071). Morphometric analyses of Ascl1 staining were performed as described [73].
Immunohistochemistry
Immunohistochemistry was performed as described [73] α-Tubb3 (AbCam), α-TH (AbCam), and α-Myc (Sigma) antibodies were used in combination with DyLight secondary antibodies (Thermo Scientific).
Immunoblotting and co-immunoprecipitation experiments
Co-immunoprecipitation experiments were performed in HEK 293 cells using α-Myc and α-Flag (Sigma) as described [73]. Rat Sox10 was affixed with an N-terminal 6X Myc-tag via cloning into pCS2+MT. Densitometry analyses were performed using BioRad Quantity One software.
Transactivation assays
Luciferase assays were performed in HeLa cells using the dual luciferase assay kit (Promega) as per manufacturer's instructions. 2 µg total DNA (0.25 µg of either pCS2-FLAG, pCS2-FLAG+Phox2b, or pRK5-FLAG+Sox10 (provided by Brian Black), 0.5 µg of either pcDNA3.1, pcDNA3.1-FLAG+Twist1[WT], or pcDNA3.1-FLAG+Twist1 S192P, 1.25 µg of PHOX2b(HindIII/NcoI)-pGL3b (provided by Diego Fornasari), and 0.125 µg of pRL-CMV) was transfected in 6-well plates using X-tremeGENE HP transfection reagent (Roche). Cell lysates were read using a 96-well micro-titer plate luminometer (Thermo Labsystems). Data represent four independent experiments. Error bars denote standard error.
Bioinformatics
All sequences were obtained via Ensembl BLASTN search (http://www.ensembl.org) using the human PHOX2b 5′ promoter as a point of reference. PATTERNMATCH and CLUSTALW analyses were performed using the SDSC Biology WorkBench (http://workbench.sdsc.edu),
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA)
EMSAs were performed as previously described [74] with minor alterations. In vitro transcription and translation of Sox10 and Twist1 mRNAs were performed using pCS2-MT+Sox10 and pCS2-MT+Twist1 expression plasmids and the TnT rabbit reticulocyte lysate in vitro transcription system (Promega) as per manufacturer's instructions. 5 µL of TnT was used per reaction. Radiolabeled, annealed probes were purified using mini Quick Spin Oligo Columns (Roche). 1 µg poly(dG-dC) was used as a nonspecific DNA-binding competitor. Reactions were incubated for 30 min at room temperature following addition of probe. The following oligos, annealed to their complements, were used: E-Box 1, 5′-ACACTCTTACAAAACAGGTTTTCTATGACATCAAGGTTTCTTC-3′; E-Box 1(Mut), 5-ACACTCTTACAAAAtgGGacTTCTATGACATCAAGGTTTCTTC-3′; HMG 3 5′-TTTCCAAGTAGTGTGATTGAATTAAAGGGCAGGGA-3′; HMG 4 5′-TGGTATTAAATTCTAATTAGAGATGCAGGAATCAATGATAGGGAGGTTGGACAGCT-3′; E-box 2, 5′-AAGACCAACCGCTTTGCTATTGTCCAAGTGGAAAGAGCCAAGTTTATTATGAGG-3′. An oligo featuring a mutated HMG Box (HMG 4(Mut) 5′-TGGTATTAAATTCTAATTAGAGATGCAGGAATatcTGATAGGGAGGTTGGACAGCT-3′) was used as an unlabeled competitor.
Ethics statement
Animal work (mouse) was performed according to an approved animal protocol from the University of Indiana IACUC, which is an AAALAC accredited program. We strive to focus on the three Rs (reduction/refinement/replacement) when working with animal models.
Supporting Information
Zdroje
1. Bronner-FraserM (1994) Neural crest cell formation and migration in the developing embryo. FASEB Journal 8 : 699–706.
2. Bronner-FraserM (1995) Origins and developmental potential of the neural crest. Experimental Cell Research 218 : 405–417.
3. JainR, RentschlerS, EpsteinJA (2010) Notch and cardiac outflow tract development. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1188 : 184–190.
4. TrainorPA (2010) Craniofacial birth defects: The role of neural crest cells in the etiology and pathogenesis of Treacher Collins syndrome and the potential for prevention. American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A 152A: 2984–2994.
5. KirbyML, GaleTF, StewartDE (1983) Neural crest cells contribute to normal aorticopulmonary septation. Science 220 : 1059–1061.
6. BrownCB, BaldwinHS (2006) Neural crest contribution to the cardiovascular system. Advances in Experimental Medicine & Biology 589 : 134–154.
7. HutsonMR, KirbyML (2007) Model systems for the study of heart development and disease. Cardiac neural crest and conotruncal malformations. Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology 18 : 101–110.
8. VincentSD, BuckinghamME (2010) How to make a heart: the origin and regulation of cardiac progenitor cells. Current Topics in Developmental Biology 90 : 1–41.
9. HowardMJ (2005) Mechanisms and perspectives on differentiation of autonomic neurons. Developmental Biology 277 : 271–286.
10. KirbyML (1989) Plasticity and predetermination of mesencephalic and trunk neural crest transplanted into the region of the cardiac neural crest. Developmental Biology 134 : 402–412.
11. WuX, HowardMJ (2001) Two signal transduction pathways involved in the catecholaminergic differentiation of avian neural crest-derived cells in vitro. Molecular & Cellular Neurosciences 18 : 394–406.
12. Nelms BL, Labosky PA (2010) Transcriptional Control of Neural Crest Development. San Rafael (CA): Morgan & Claypool Life Sciences.
13. QianQ, YoungX, TaoH, ChunlinQ, JianmingX (2011) Normal and disease-related biological functions of Twist1 and underlying molecular mechanisms. Cell Research 90–116.
14. VincentzJW, BarnesRM, RodgersR, FirulliBA, ConwaySJ, et al. (2008) An Absence of Twist1 results in aberrant cardiac neural crest morphogenesis. Dev Biol 320 : 131–139.
15. JiangX, IsekiS, MaxsonRE, SucovHM, Morriss-KayGM (2002) Tissue origins and interactions in the mammalian skull vault. Developmental Biology 241 : 106–116.
16. BarnesRM, FirulliB, ConwaySJ, VincentzJW, FirulliAB (2010) Analysis of the Hand1 Cell Lineage Reveals Novel Contributions to Cardiovascular,Neural Crest, Extra-Embryonic, and Lateral Mesoderm Derivatives. Dev Dyn 239 : 3086–3097.
17. KimJ, LoL, DormandE, AndersonDJ (2003) SOX10 maintains multipotency and inhibits neuronal differentiation of neural crest stem cells. Neuron 38 : 17–31.
18. BiakelP, KernB, yangX, SchrockM, SosicD, et al. (2004) A Twist code determines the onset of osteoblast differentiation. Dev Cell 6 : 423–435.
19. HowardM, FosterDN, CserjesiP (1999) Expression of HAND gene products may be sufficient for the differentiation of avian neural crest-derived cells into catecholaminergic neurons in culture. Developmental Biology 215 : 62–77.
20. CserjesiP, BrownD, LyonsGE, OlsonEN (1995) Expression of the novel basic helix-loop-helix gene eHAND in neural crest derivatives and extraembryonic membranes during mouse development. Dev Biol 170 : 664–678.
21. StankeM, JunghansD, GeissenM, GoridisC, ErnsbergerU, et al. (1999) The Phox2 homeodomain proteins are sufficient to promote the development of sympathetic neurons. Development 126 : 4087–4094.
22. StankeM, StubbuschJ, RohrerH (2004) Interaction of Mash1 and Phox2b in sympathetic neuron development. Molecular & Cellular Neurosciences 25 : 374–382.
23. TsarovinaK, PattynA, StubbuschJ, MullerF, van der WeesJ, et al. (2004) Essential role of Gata transcription factors in sympathetic neuron development. Development 131 : 4775–4786.
24. BurauK, StenullI, HuberK, MisawaH, BerseB, et al. (2004) c-ret regulates cholinergic properties in mouse sympathetic neurons: evidence from mutant mice. Eur J Neurosci 20 : 353–362.
25. FirulliAB, McFaddenDG, LinQ, SrivastavaD, OlsonEN (1998) Heart and extra-embryonic mesodermal defects in mouse embryos lacking the bHLH transcription factor Hand1. Nature Genetics 18 : 266–270.
26. HendershotTJ, LiuH, ClouthierDE, ShepherdIT, CoppolaE, et al. (2008) Conditional deletion of Hand2 reveals critical functions in neurogenesis and cell type-specific gene expression for development of neural crest-derived noradrenergic sympathetic ganglion neurons. Developmental Biology 319 : 179–191.
27. FeinerL, WebberAL, BrownCB, LuMM, JiaL, et al. (2001) Targeted disruption of semaphorin 3C leads to persistent truncus arteriosus and aortic arch interruption. Development 128 : 3061–3070.
28. BrownCB, FeinerL, LuMM, LiJ, MaX, et al. (2001) PlexinA2 and semaphorin signaling during cardiac neural crest development. Development 128 : 3071–3080.
29. LeeMP, YutzeyKE (2011) Twist1 directly regulates genes that promote cell proliferation and migration in developing heart valves. PLoS ONE 6: e29758 doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0029758
30. SooK, O'RourkeMP, KhooP-L, SteinerKA, WongN, et al. (2002) Twist function is required for the morphogenesis of the cephalic neural tube and the differentiation of the cranial neural crest cells in the mouse embryo. Developmental Biology 247 : 251–270.
31. LucasME, MullerF, RudigerR, HenionPD, RohrerH (2006) The bHLH transcription factor hand2 is essential for noradrenergic differentiation of sympathetic neurons. Development 133 : 4015–4024.
32. MorikawaY, D'AutreauxF, GershonMD, CserjesiP (2007) Hand2 determines the noradrenergic phenotype in the mouse sympathetic nervous system. Developmental Biology 307 : 114–126.
33. FirulliBA, KrawchukD, CentonzeVE, VirshupDE, ConwaySJ, et al. (2005) Altered Twist1 and Hand2 dimerization is associated with Saethre-Chotzen syndrome and limb abnormalities. Nat Genet 37 : 373–381.
34. VincentzJW, VanDusenNJ, FlemingAB, RubartM, FirulliBA, et al. (2012) A Phox2 - and Hand2-dependent Hand1 cis-regulatory element reveals a unique gene dosage requirement for Hand2 during sympathetic neurogenesis. J Neuro Sci 32 : 2110–2120.
35. XuH, FirulliAB, WuX, ZhangX, HowardMJ (2003) HAND2 synergistically enhances transcription of dopamine-_B-hydroxylase in the presence of Phox2a. Dev Biol 262 : 183–193.
36. HowardMJ, StankeM, SchneiderC, WuX, RohrerH (2000) The transcription factor dHAND is a downstream effector of BMPs in sympathetic neuron specification. Development 127 : 4073–4081.
37. GuS, BoyerTG, NaskiMC (2012) Basic helix-loop-helix transcription factor twist1 inhibits the transacivator function of the master chondrogenic regulator Sox9. J Biol Chem Epub ahead of print
38. WegnerM (1999) From head to toes: the multiple facets of Sox proteins. Nucleic Acids Research 27 : 1409–1420.
39. FirulliBA, RedickBA, ConwaySJ, FirulliAB (2007) Mutations within helix I of Twist1 result in distinct limb defects and variation of DNA binding affinities. Journal of Biological Chemistry 282 : 27536–27546.
40. ConnerneyJ, AndreevaV, LeshemY, MuentenerC, MercadoMA, et al. (2006) Twist1 dimer selection regulates cranial suture patterning and fusion. Developmental Dynamics 235 : 1345–1357.
41. PaznekasWA, CunninghamML, HowardTD, KorfBR, LipsonMH, et al. (1998) Genetic heterogeneity of Saethre-Chotzen syndrome, due to TWIST and FGFR mutations. Am J Hum Genet 62 : 1370–1380.
42. RoseCS, PatelP, ReardonW, MalcolmS, WinterRM (1997) The TWIST gene, although not disrupted in Saethre-Chotzen patients with apparently balanced translocations of 7p21, is mutated in familial and sporadic cases. Hum Mol Genet 6 : 1369–1373.
43. HamamoriY, WuHY, SartorelliV, KedesL (1997) The basic domain of myogenic basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) proteins is the novel target for direct inhibition by another bHLH protein, Twist. Molecular & Cellular Biology 17 : 6563–6573.
44. El GhouzziV, Legeai-MalletL, Benoist-LasselinC, LajeunieE, RenierD, et al. (2001) Mutations in the basic domain and the loop-helix II junction of TWIST abolish DNA binding in Saethre-Chotzen syndrome. FEBS Lett 492 : 112–118.
45. BarnesRM, FirulliAB (2009) A Twist of insight, the role of Twist-Family bHLH factors in development. Int J Dev Biol 53 : 909–924.
46. PhamD, VincentzJW, FirulliAB, KaplanMH (2012) Twist1 regulates Ifng expression in Th1 cells by interfering with Runx3 function. J Immunol In press.
47. YamauchiY, AbeK, MantaniA, HitoshiY, SuzukiM, et al. (1999) A novel transgenic technique that allows specific marking of the neural crest cell lineage in mice. Developmental Biology 212 : 191–203.
48. JiangX, RowitchDH, SorianoP, McMahonAP, SucovHM (2000) Fate of the mammalian cardiac neural crest. Development 127 : 1607–1616.
49. PietriT, EderO, BlancheM, ThieryJP, DufourS (2003) The human tissue plasminogen activator-Cre mouse: a new tool for targeting specifically neural crest cells and their derivatives in vivo. Dev Biol 259 : 176–187.
50. HildrethV, WebbS, BradshawL, BrownNA, AndersonRH, et al. (2008) Cells migrating from the neural crest contribute to the innervation of the venous pole of the heart. Journal of anatomy 212 : 1–11.
51. CreazzoTL, GodtRE, LeatherburyL, ConwaySJ, KirbyML (1998) Role of cardiac neural crest cells in cardiovascular development. Annu Rev Physiol 60 : 267–286.
52. MauhinV, LutzY, DennefeldC, AlbergaA (1993) Definition of the DNA-binding site repertoire for the Drosophila transcription factor SNAIL. Nucleic Acids Res 21 : 3951–3957.
53. VincentT, NeveEP, JohnsonJR, KukalevA, RojoF, et al. (2009) A SNAIL1-SMAD3/4 transcriptional repressor complex promotes TGF-beta mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Cell Biol 11 : 943–950.
54. Reece-HoyesJS, DeplanckeB, BarrasaMI, HatzoldJ, SmitRB, et al. (2009) The C. elegans Snail homolog CES-1 can activate gene expression in vivo and share targets with bHLH transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res 37 : 3689–3698.
55. OramKF, GridleyT (2005) Mutations in snail family genes enhance craniosynostosis of Twist1 haplo-insufficient mice: implications for Saethre-Chotzen Syndrome. Genetics 170 : 971–974.
56. LeptinM (1991) Twist and snail as positive and negative regulators during Drosophila mesoderm development. Genes & Development 5 : 1568–1576.
57. CheungM, ChaboissierMC, MynettA, HirstE, SchedlA, et al. (2005) The transcriptional control of trunk neural crest induction, survival, and delamination. Developmental Cell 8 : 179–192.
58. RaidR, KrinkaD, BakhoffL, AbdelwahidE, JokinenE, et al. (2009) Lack of Gata3 results in conotruncal heart anomalies in mouse. Mechanisms of Development 126 : 80–89.
59. SchilhamMW, OosterwegelMA, MoererP, YaJ, de BoerPA, et al. (1996) Defects in cardiac outflow tract formation and pro-B-lymphocyte expansion in mice lacking Sox-4. Nature 380 : 711–714.
60. SockE, RettigSD, EnderichJ, BoslMR, TammER, et al. (2004) Gene targeting reveals a widespread role for the high-mobility-group transcription factor Sox11 in tissue remodeling. Mol Cell Biol 24 : 6635–6644.
61. PotznerMR, TsarovinaK, BinderE, Penzo-MendezA, LefebvreV, et al. (2010) Sequential requirement of Sox4 and Sox11 during development of the sympathetic nervous system. Development 137 : 775–784.
62. AnsieauS, MorelAP, HinkalG, BastidJ, PuisieuxA (2010) TWISTing an embryonic transcription factor into an oncoprotein. Oncogene 29 : 3173–3184.
63. YangJ, ManiSA, DonaherJL, RamaswamyS, ItzyksonRA, et al. (2004) Twist, a master regulator of morphogenesis, plays an essential role in tumor metastasis. Cell 117 : 927–939.
64. Valsesia-WittmannS, MagdeleineM, DupasquierS, GarinE, JallasAC, et al. (2004) Oncogenic cooperation between H-Twist and N-Myc overrides failsafe programs in cancer cells. Cancer cell 6 : 625–630.
65. WaldmannJ, SlaterEP, LangerP, BuchholzM, RamaswamyA, et al. (2009) Expression of the transcription factor snail and its target gene twist are associated with malignancy in pheochromocytomas. Annals of surgical oncology 16 : 1997–2005.
66. ChenZF, Behringer (1995) Twist is required in head mesenchyme for cranial neural tube morphogenesis. Genes Dev 9 : 686–699.
67. ChenYT, AkinwunmiPO, DengJM, TamOH, BehringerRR (2007) Generation of a Twist1 conditional null allele in the mouse. Genesis: the Journal of Genetics & Development 45 : 588–592.
68. JiangX, ChoudharyB, MerkiE, ChienKR, MaxsonRE, et al. (2002) Normal fate and altered function of the cardiac neural crest cell lineage in retinoic acid receptor mutant embryos. Mechanisms of Development 117 : 115–122.
69. McFaddenDG, BarbosaAC, RichardsonJA, SchneiderMD, SrivastavaD, et al. (2005) The Hand1 and Hand2 transcription factors regulate expansion of the embryonic cardiac ventricles in a gene dosage-dependent manner. Development 132 : 189–201.
70. SorianoP (1999) Generalized lacZ expression with the ROSA26 Cre reporter strain. Nat Genet 21 : 70–71.
71. PattynA, MorinX, CremerH, GoridisC, BrunetJF (1999) The homeobox gene Phox2b is essential for the development of autonomic neural crest derivatives. Nature 399 : 366–370.
72. BarnesRM, FirulliBA, VanDusenNJ, MorikawaY, ConwaySJ, et al. (2011) Hand2 loss-of-function in Hand1-expressing cells Reveals Distinct Roles in Epicardial and Coronary Vessel Development. Circ Res 108 : 940–949.
73. VincentzJW, BarnesRM, FirulliBA, ConwaySJ, FirulliAB (2008) Cooperative interaction of Nkx2.5 and Mef2c transcription factors during heart development. Developmental Dynamics 237 : 3809–3819.
74. DodouE, XuSM, BlackBL (2003) mef2c is activated directly by myogenic basic helix-loop-helix proteins during skeletal muscle development in vivo. Mech Dev 120 : 1021–1032.
Štítky
Genetika Reprodukční medicína
Článek Ubiquitous Polygenicity of Human Complex Traits: Genome-Wide Analysis of 49 Traits in KoreansČlánek Alternative Splicing and Subfunctionalization Generates Functional Diversity in Fungal ProteomesČlánek RFX Transcription Factor DAF-19 Regulates 5-HT and Innate Immune Responses to Pathogenic Bacteria inČlánek Surveillance-Activated Defenses Block the ROS–Induced Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein ResponseČlánek Deficiency Reduces Adipose OXPHOS Capacity and Triggers Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Mice
Článek vyšel v časopisePLOS Genetics
Nejčtenější tento týden
2013 Číslo 3- Akutní intermitentní porfyrie
- Souvislost haplotypu M2 genu pro annexin A5 s opakovanými reprodukčními ztrátami
- Příjem alkoholu a menstruační cyklus
- Doporučení pro diagnostiku a léčbu akutních jaterních porfyrií
- Doc. Miloš Kubánek: Nemocní se srdeční amyloidózou jsou často skryti a sledováni pod jinými diagnózami
-
Všechny články tohoto čísla
- Power and Predictive Accuracy of Polygenic Risk Scores
- Rare Copy Number Variants Are a Common Cause of Short Stature
- Coordination of Flower Maturation by a Regulatory Circuit of Three MicroRNAs
- Ubiquitous Polygenicity of Human Complex Traits: Genome-Wide Analysis of 49 Traits in Koreans
- Genomic Evidence for Island Population Conversion Resolves Conflicting Theories of Polar Bear Evolution
- Mechanistic Insight into the Pathology of Polyalanine Expansion Disorders Revealed by a Mouse Model for X Linked Hypopituitarism
- Genome-Wide Association Study and Gene Expression Analysis Identifies as a Predictor of Response to Etanercept Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Problem Solved: An Interview with Sir Edwin Southern
- Long Interspersed Element–1 (LINE-1): Passenger or Driver in Human Neoplasms?
- Mouse HFM1/Mer3 Is Required for Crossover Formation and Complete Synapsis of Homologous Chromosomes during Meiosis
- Alternative Splicing and Subfunctionalization Generates Functional Diversity in Fungal Proteomes
- A WRKY Transcription Factor Recruits the SYG1-Like Protein SHB1 to Activate Gene Expression and Seed Cavity Enlargement
- Microhomology-Mediated Mechanisms Underlie Non-Recurrent Disease-Causing Microdeletions of the Gene or Its Regulatory Domain
- Ancient Evolutionary Trade-Offs between Yeast Ploidy States
- Differential Evolutionary Fate of an Ancestral Primate Endogenous Retrovirus Envelope Gene, the EnvV , Captured for a Function in Placentation
- A Feed-Forward Loop Coupling Extracellular BMP Transport and Morphogenesis in Wing
- The Tomato Yellow Leaf Curl Virus Resistance Genes and Are Allelic and Code for DFDGD-Class RNA–Dependent RNA Polymerases
- The U-Box E3 Ubiquitin Ligase TUD1 Functions with a Heterotrimeric G α Subunit to Regulate Brassinosteroid-Mediated Growth in Rice
- Role of the DSC1 Channel in Regulating Neuronal Excitability in : Extending Nervous System Stability under Stress
- –Independent Phenotypic Switching in and a Dual Role for Wor1 in Regulating Switching and Filamentation
- Pax6 Regulates Gene Expression in the Vertebrate Lens through miR-204
- Blood-Informative Transcripts Define Nine Common Axes of Peripheral Blood Gene Expression
- Genetic Architecture of Skin and Eye Color in an African-European Admixed Population
- Fine Characterisation of a Recombination Hotspot at the Locus and Resolution of the Paradoxical Excess of Duplications over Deletions in the General Population
- Estrogen Mediated-Activation of miR-191/425 Cluster Modulates Tumorigenicity of Breast Cancer Cells Depending on Estrogen Receptor Status
- Complex Patterns of Genomic Admixture within Southern Africa
- Yap- and Cdc42-Dependent Nephrogenesis and Morphogenesis during Mouse Kidney Development
- Molecular Networks of Human Muscle Adaptation to Exercise and Age
- Alp/Enigma Family Proteins Cooperate in Z-Disc Formation and Myofibril Assembly
- Polycomb Group Gene Regulates Rice () Seed Development and Grain Filling via a Mechanism Distinct from
- RFX Transcription Factor DAF-19 Regulates 5-HT and Innate Immune Responses to Pathogenic Bacteria in
- Distinct Molecular Strategies for Hox-Mediated Limb Suppression in : From Cooperativity to Dispensability/Antagonism in TALE Partnership
- A Natural Polymorphism in rDNA Replication Origins Links Origin Activation with Calorie Restriction and Lifespan
- TDP2–Dependent Non-Homologous End-Joining Protects against Topoisomerase II–Induced DNA Breaks and Genome Instability in Cells and
- Recurrent Rearrangement during Adaptive Evolution in an Interspecific Yeast Hybrid Suggests a Model for Rapid Introgression
- Genome-Wide Association Study in Mutation Carriers Identifies Novel Loci Associated with Breast and Ovarian Cancer Risk
- Coincident Resection at Both Ends of Random, γ–Induced Double-Strand Breaks Requires MRX (MRN), Sae2 (Ctp1), and Mre11-Nuclease
- Identification of a -Specific Modifier Locus at 6p24 Related to Breast Cancer Risk
- A Novel Function for the Hox Gene in the Male Accessory Gland Regulates the Long-Term Female Post-Mating Response in
- Tdp2: A Means to Fixing the Ends
- A Novel Role for the RNA–Binding Protein FXR1P in Myoblasts Cell-Cycle Progression by Modulating mRNA Stability
- Association Mapping and the Genomic Consequences of Selection in Sunflower
- Histone Deacetylase 2 (HDAC2) Regulates Chromosome Segregation and Kinetochore Function via H4K16 Deacetylation during Oocyte Maturation in Mouse
- A Novel Mutation in the Upstream Open Reading Frame of the Gene Causes a MEN4 Phenotype
- Ataxin1L Is a Regulator of HSC Function Highlighting the Utility of Cross-Tissue Comparisons for Gene Discovery
- Human Spermatogenic Failure Purges Deleterious Mutation Load from the Autosomes and Both Sex Chromosomes, including the Gene
- A Conserved Upstream Motif Orchestrates Autonomous, Germline-Enriched Expression of piRNAs
- Statistical Analysis Reveals Co-Expression Patterns of Many Pairs of Genes in Yeast Are Jointly Regulated by Interacting Loci
- Matefin/SUN-1 Phosphorylation Is Part of a Surveillance Mechanism to Coordinate Chromosome Synapsis and Recombination with Meiotic Progression and Chromosome Movement
- A Role for the Malignant Brain Tumour (MBT) Domain Protein LIN-61 in DNA Double-Strand Break Repair by Homologous Recombination
- The Population and Evolutionary Dynamics of Phage and Bacteria with CRISPR–Mediated Immunity
- Long Noncoding RNA MALAT1 Controls Cell Cycle Progression by Regulating the Expression of Oncogenic Transcription Factor B-MYB
- Surveillance-Activated Defenses Block the ROS–Induced Mitochondrial Unfolded Protein Response
- DNA Topoisomerase III Localizes to Centromeres and Affects Centromeric CENP-A Levels in Fission Yeast
- Genome-Wide Control of RNA Polymerase II Activity by Cohesin
- Divergent Selection Drives Genetic Differentiation in an R2R3-MYB Transcription Factor That Contributes to Incipient Speciation in
- NODULE INCEPTION Directly Targets Subunit Genes to Regulate Essential Processes of Root Nodule Development in
- Spreading of a Prion Domain from Cell-to-Cell by Vesicular Transport in
- Deficiency in Origin Licensing Proteins Impairs Cilia Formation: Implications for the Aetiology of Meier-Gorlin Syndrome
- Deficiency Reduces Adipose OXPHOS Capacity and Triggers Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Mice
- The Conserved SKN-1/Nrf2 Stress Response Pathway Regulates Synaptic Function in
- Functional Genomic Analysis of the Regulatory Network in
- Astakine 2—the Dark Knight Linking Melatonin to Circadian Regulation in Crustaceans
- CRL2 E3-Ligase Regulates Proliferation and Progression through Meiosis in the Germline
- Both the Caspase CSP-1 and a Caspase-Independent Pathway Promote Programmed Cell Death in Parallel to the Canonical Pathway for Apoptosis in
- PRMT4 Is a Novel Coactivator of c-Myb-Dependent Transcription in Haematopoietic Cell Lines
- A Copy Number Variant at the Locus Likely Confers Risk for Canine Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Digit
- Evidence of Gene–Environment Interactions between Common Breast Cancer Susceptibility Loci and Established Environmental Risk Factors
- HIV Infection Disrupts the Sympatric Host–Pathogen Relationship in Human Tuberculosis
- Trans-Ethnic Fine-Mapping of Lipid Loci Identifies Population-Specific Signals and Allelic Heterogeneity That Increases the Trait Variance Explained
- A Gene Transfer Agent and a Dynamic Repertoire of Secretion Systems Hold the Keys to the Explosive Radiation of the Emerging Pathogen
- The Role of ATM in the Deficiency in Nonhomologous End-Joining near Telomeres in a Human Cancer Cell Line
- Dynamic Circadian Protein–Protein Interaction Networks Predict Temporal Organization of Cellular Functions
- Nuclear Myosin 1c Facilitates the Chromatin Modifications Required to Activate rRNA Gene Transcription and Cell Cycle Progression
- Robust Prediction of Expression Differences among Human Individuals Using Only Genotype Information
- A Single Cohesin Complex Performs Mitotic and Meiotic Functions in the Protist
- The Role of the Arabidopsis Exosome in siRNA–Independent Silencing of Heterochromatic Loci
- Elevated Expression of the Integrin-Associated Protein PINCH Suppresses the Defects of Muscle Hypercontraction Mutants
- Twist1 Controls a Cell-Specification Switch Governing Cell Fate Decisions within the Cardiac Neural Crest
- Genome-Wide Testing of Putative Functional Exonic Variants in Relationship with Breast and Prostate Cancer Risk in a Multiethnic Population
- Heteroduplex DNA Position Defines the Roles of the Sgs1, Srs2, and Mph1 Helicases in Promoting Distinct Recombination Outcomes
- PLOS Genetics
- Archiv čísel
- Aktuální číslo
- Informace o časopisu
Nejčtenější v tomto čísle- Fine Characterisation of a Recombination Hotspot at the Locus and Resolution of the Paradoxical Excess of Duplications over Deletions in the General Population
- Molecular Networks of Human Muscle Adaptation to Exercise and Age
- Recurrent Rearrangement during Adaptive Evolution in an Interspecific Yeast Hybrid Suggests a Model for Rapid Introgression
- Genome-Wide Association Study and Gene Expression Analysis Identifies as a Predictor of Response to Etanercept Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Kurzy
Zvyšte si kvalifikaci online z pohodlí domova
Autoři: prof. MUDr. Vladimír Palička, CSc., Dr.h.c., doc. MUDr. Václav Vyskočil, Ph.D., MUDr. Petr Kasalický, CSc., MUDr. Jan Rosa, Ing. Pavel Havlík, Ing. Jan Adam, Hana Hejnová, DiS., Jana Křenková
Autoři: MUDr. Irena Krčmová, CSc.
Autoři: MDDr. Eleonóra Ivančová, PhD., MHA
Všechny kurzyPřihlášení#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Zapomenuté hesloZadejte e-mailovou adresu, se kterou jste vytvářel(a) účet, budou Vám na ni zaslány informace k nastavení nového hesla.
- Vzdělávání



