-
Medical journals
- Career
Traumatizace rány při chirurgickém débridementu – experimentální studie
Authors: Jan Stryja
Authors‘ workplace: Vzdělávací a výzkumný institut AGEL, o. p. s., Třinec ; Komplexní kardiovaskulární centrum, Nemocnice Podlesí a. s., Třinec.
Published in: Hojení ran 8, č. 1: 37-42, 2014
Category: Debridement
Overview
Chirurgický débridement rány je součástí řady klinických standardů a doporučených postupů. Smyslem chirurgického débridementu je za pomoci chirurgických (ostrých) nástrojů odstranit ze spodiny rány nekrotické části tkáně a povlaky, cizí tělesa, ulpívající zbytky terapeutických krytí a přestárlé buňky, které již nejsou schopny reprodukce a podílí se tak na stagnaci hojení rány. Na základě empirických poznatků lze usuzovat, že různé techniky a metody chirurgického débridementu způsobují různý stupeň traumatizace spodiny a okolí rány. Cílem experimentální studie je objektivizovat míru traumatizace tkáně na spodině testované rány při použití čtyř nejčastěji využívaných technik ostrého débridementu: chirurgických nůžek, skalpelu, elektrokauteru a hydrochirurgického nástroje (Versajet) na základě stanovení mikroskopických markerů stupně poškození. V rámci výzkumu bylo histopatologicky zhodnoceno 128 vzorků tkání ze spodiny modelu ran ošetřených pomocí čtyř výše uvedených technik ostrého débridementu. Stupeň traumatizace tkáně popsaný v jednotlivých skupinách byl statisticky zpracován a výsledky jednotlivých technik byly vzájemně porovnány. Z analýzy dat vyplývá, že débridement modelové ulcerace provedený pomocí hydrochirurgie dosahuje nižší úrovně traumatizace tkáně než nůžky a elektrokauter (p=0,00013, p=0,00145). V míře traumatizace tkáně ošetřené skalpelem a hydrochirurgicky nebyl nalezen statisticky významný rozdíl (p=0,17775). Výzkum prokázal přesnost a bezpečnost hydrochirurgické metody débridementu a débridementu pomocí skalpelu. Použití chirurgických nůžek vede prokazatelně k vyšší traumatizaci spodiny rány i okolí, je neselektivní a spolu s použitím elektrokauteru zvyšuje výskyt sekundárních nekróz na spodině jimi ošetřených ulcerací.
Klíčová slova:
ostrý débridement, traumatizace tkáně, skalpel, nůžky, elektrokauter, hydrochirurgieÚvod
Reparace tkáně je časově náročný proces probíhající in vivo, který je závislý na správné funkci řady tělesných systémů. Nedostatečná selektivita různých forem chirurgického débridementu může být příčinou poškození vitální spodiny rány a paradoxně může zpomalovat hojení rány. Přímé stanovení stupně traumatizace tkání na spodině rány pomocí biopsie a histologického vyšetření vzorku může být ovlivněno lokálními anatomickými podmínkami, předchozím hojením v minulosti poškozené tkáně a dalšími nestandardními podmínkami. Provedení biopsie u končetiny potenciálně ohrožené amputací navíc nelze považovat za postup lege artis. K realizaci experimentu proto byla naplánována prospektivní randomizovaná studie hodnotící úroveň traumatizace na základě histologického vyšetření modelového vzorku tkáně – ex vivo. Práce, navržená jako prospektivní zaslepená srovnávací studie, zkoumá rozsah poškození spodiny rány čtyřmi formami chirurgického débridementu na modelu operační rány.
Ostrý débridement patří mezi preferované metody débridementu ulcerací u diabetiků (Goode 1995; NICE 2001). I přes tato jednoznačná doporučení se však zatím nepodařilo význam débridementu prokázat prostřednictvím Cochranovy metaanalýzy (Lebrun et al. 2010). Selektivní razantní débridement rány respektující požadavek na minimální traumatizaci hlubších (vitálních) struktur na spodině rány dává předpoklady pro zkrácení zánětlivé fáze hojení a tím i ke zrychlení hojení ulcerace samotné. Rozsáhlá traumatizace spodiny rány vede naopak k narušení vitality spodiny s rizikem ischemizace okrajů rány a prohloubení nekrózy měkkých tkání. Nedostatečná selektivita výkonu provázená rizikem overexcize tkání na spodině rány při provádění ostrého a chirurgického débridementu daná různou úrovní zkušeností a zručnosti operatéra je příčinou rozdílné účinnosti, interindividuální oblíbenosti i frekvence použití chirurgického débridementu v praxi.
Při výběru vhodné metody hodnocení histopatologických změn spojených s prováděním débridementu na tkáňovém modelu jsme vycházeli mimo jiné z poznatků klinické studie zaměřené na léčbu popálenin v oblasti krku a obličeje (Tenenhaus et al. 2007). Tenenhaus zkoumal pomocí prospektivní klinické studie univerzálnost použití hydrochirurgie v léčbě hlubokých popálenin na krku a na obličeji. Ve svém experimentu provedl nejprve débridement kožní tkáně Versajetem a následně měřil mikrometricky jeho hloubku pomocí světelné mikroskopie. Takto zaznamenal tloušťku odstraněné tkáně. Při použití stupně nastavení sedm a osm byla odstraněna dermis o síle osmdesáti až sto mikrometrů. Tenenhaus prokázal (Tenenhaus et al. 2007), že hydrochirurgický systém Versajet umožňuje provedení šetrného débridementu plošných povrchních popálenin se zachováním kožních adnex na spodině rány a označil ošetření rány hydrochirurgickým débridementem za šetrné. Jeho experiment demonstroval, že pomocí hydrochirurgie je možné poměrně přesně dosáhnout a ovládat hloubku provedeného débridementu (s ohledem na typ ošetřované tkáně).
Studie porovnávající efekt různých typů chirurgického débridementu na cílovou tkáň dosud zveřejněna nebyla. Pro účely výzkumu jsme se rozhodli klasifikovat celistvost testovaného okraje vzorku na základě mikroskopického hodnocení série řezů zkoumaného vzorku tkáně. Jeho hlavním cílem byla objektivizace míry poškození měkkých tkání na spodině tkáňového modelu rány při použití čtyř technik ostrého débridementu a vzájemné porovnání stupně traumatizace. V rámci výzkumu jsme hodnotili celistvost okraje vzorku tkáně pomocí histologického porovnání kvality resekčních ploch vzorků tkání po provedeném débridementu za použití skalpelu, chirurgických nůžek, elektrokauteru a handpiece Versajetu. Výzkum jsme uskutečnili provedením definované formy débridementu na vzorcích tkání získaných od pacientů léčených v Centru cévní a miniinvazivní chirurgie, Nemocnice Podlesí v Třinci. Ošetřené vzorky byly následně odeslány k histologickému zpracování na oddělení patologie, Nemocnice Nový Jičín.
Metodika
Odebraný biologický materiál jednoho pacienta byl použit k získání osmi tkáňových vzorků (tj. po dvou tkáňových bločcích v každé ze čtyř skupin débridementu). Každý zpracovaný tkáňový bloček byl prokrájen sérií řezů orientovaných na resekční okraje značené tuší. Pro zhodnocení míry traumatizace tkáně byly vybrány z každého bločku dva řezy z různých částí biopsie. V rámci experimentu bylo odebráno celkem šedesát čtyři bioptických vzorků tkání osmi pacientů. Z těchto vzorků bylo v bioptické laboratoři zhotoveno a vyšetřeno celkem sto dvacet osm histologických řezů. V každé sledované skupině (S – skalpel, V – Versajet, E – elektrokauter, N – nůžky) jsme dosáhli počtu celkem šestnácti vzorků tkáně, které byly prokrájeny sérií dvou řezů orientovaných na resekční okraje. V každé sledované skupině jsme tak k histologickému zpracování získali celkem třicet dva řezů.
K objektivizaci míry traumatizace ošetřeného vzorku tkáně při použití různých metod débridementu (a tedy i bezpečnosti použití čtyř vybraných technik ostrého débridementu) na tkáňovém modelu jsme navrhli nový systém klasifikace poškození měkkých tkání a kůže (Stryja 2012), který jsme označili jako TDD (Tissue Damage Degree). Zařazení vzorku do konkrétního stupně TDD bylo provedeno zaslepeně patologem na základě přítomnosti některého ze šesti markerů typických pro mechanické či termické poškození povrchu studované tkáně. Opodstatněnost tohoto systému byla potvrzena statistickou analýzou vzorků zkoumaných tkání. Statistická analýza výsledků experimentu potvrdila naši dřívější klinickou zkušenost, že skalpel umožňuje provést dokonalý řez a dává teoretické předpoklady pro rychlejší a kvalitnější hojení rány než nůžky nebo elektrokauter. Débridement provedený hydrochirurgickou technikou poskytoval velmi podobné výsledky jako použití skalpelu. Hydrochirurgie i elektrokauter jsou metody závislé na nastavení odpovídajícího stupně výkonu s ohledem na typ ošetřované tkáně. Toto technické nastavení (viz metodika) jsme provedli podle pokynů výrobce konkrétního zařízení a našich klinických zkušeností s metodou. Technické nastavení při débridementu bylo ve všech případech testované skupiny stejné. Statistická analýza hodnoty indexu poškození tkáně (TDD) pro každou testovanou skupinu popsala dopad débridementu na spodinu rány. Patologem hodnocené známky traumatu v oblasti resekčních okrajů shrnuje tabulka č. 1.
Table 1. Sledované markery traumatu v mikroskopickém obraze 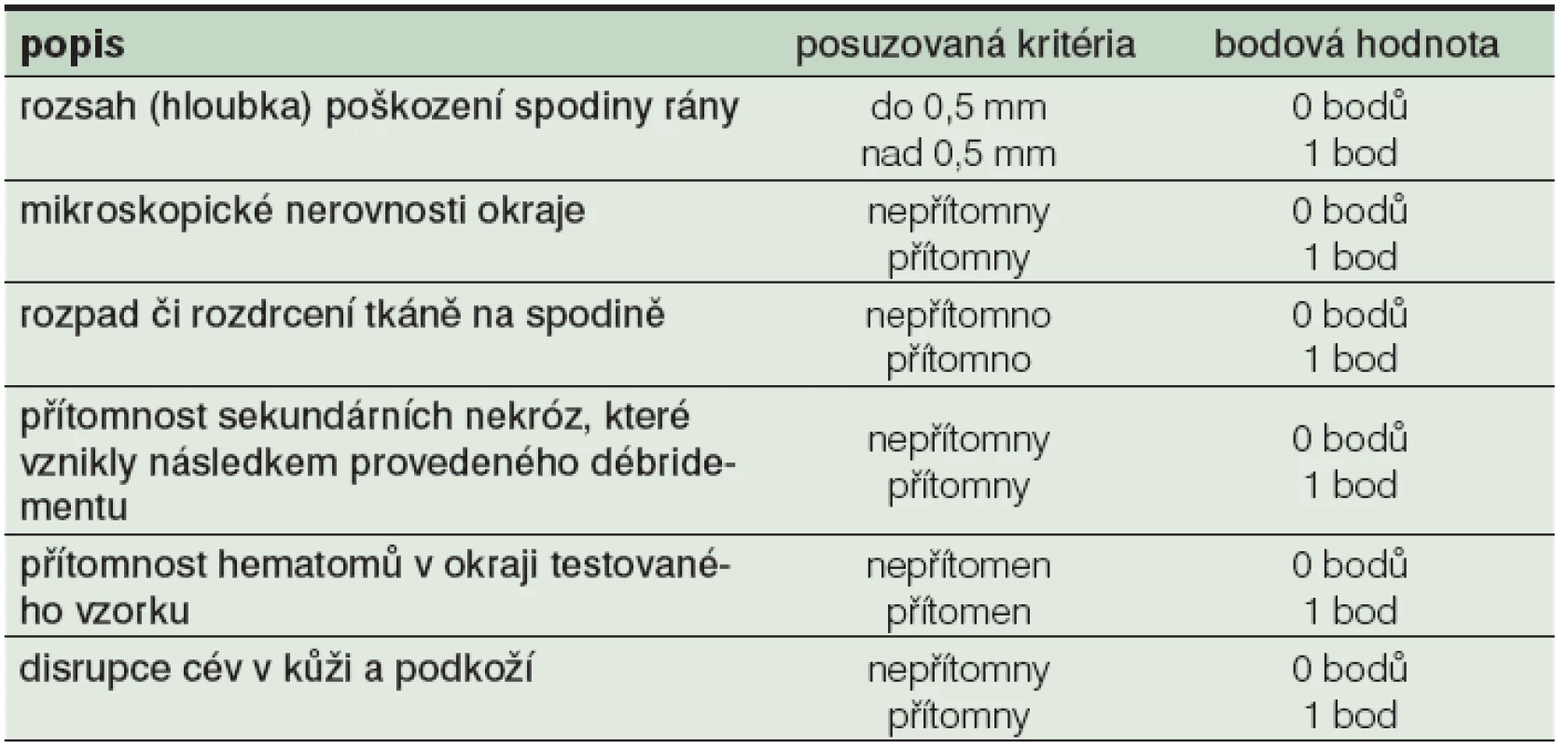
Při mikroskopickém hodnocení řezu byl konkrétní histopatologický nález extrapolován do tissue damage degree (TDD) skórovacího systému, který zohledňoval šest výše uvedených kritérií. V případě přítomnosti některého z kritérií 1–6 při mikroskopickém zhodnocení vzorků byl do hodnocení započítán jeden bod, maximálně bylo tedy možné přiřadit šest bodů. Námi použitý skórovací systém TDD rozlišuje tři stupně poškození povrchu rány (stupeň I, II a III), které odpovídají rozsahu traumatizace spodiny rány, viz tabulka č. 2.
Table 2. Skórovací systém (TDD) tissue damage degree 
Do I. stupně traumatizace, TDD I – nález zcela rovných okrajů bez trhlin nebo jiných známek zhmoždění – byly zařazeny vzorky se součtem jeden a dva body (mikroskopický obraz viz obrázky 1 a 2).
Image 1. Stupeň TDD I – zcela rovné okraje bez trhlin a zhmoždění 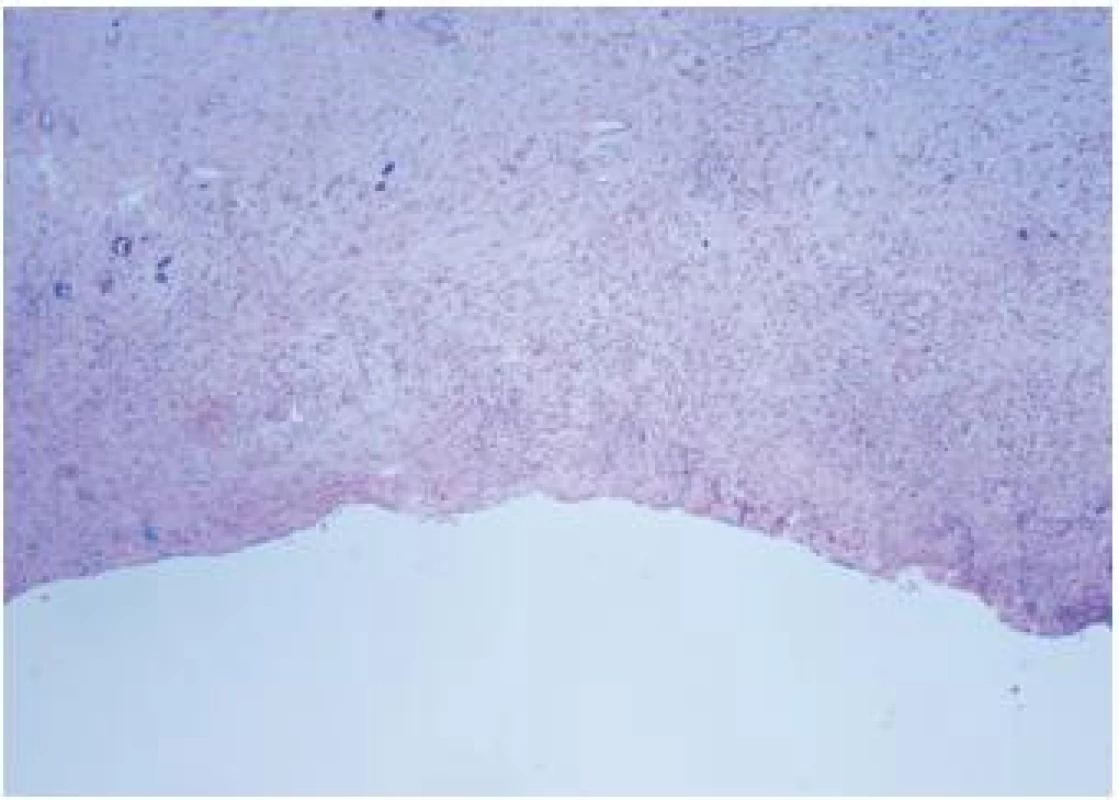
Obrázek z archivu autora Image 2. Stupeň TDD I – zcela rovné okraje bez trhlin a zhmoždění 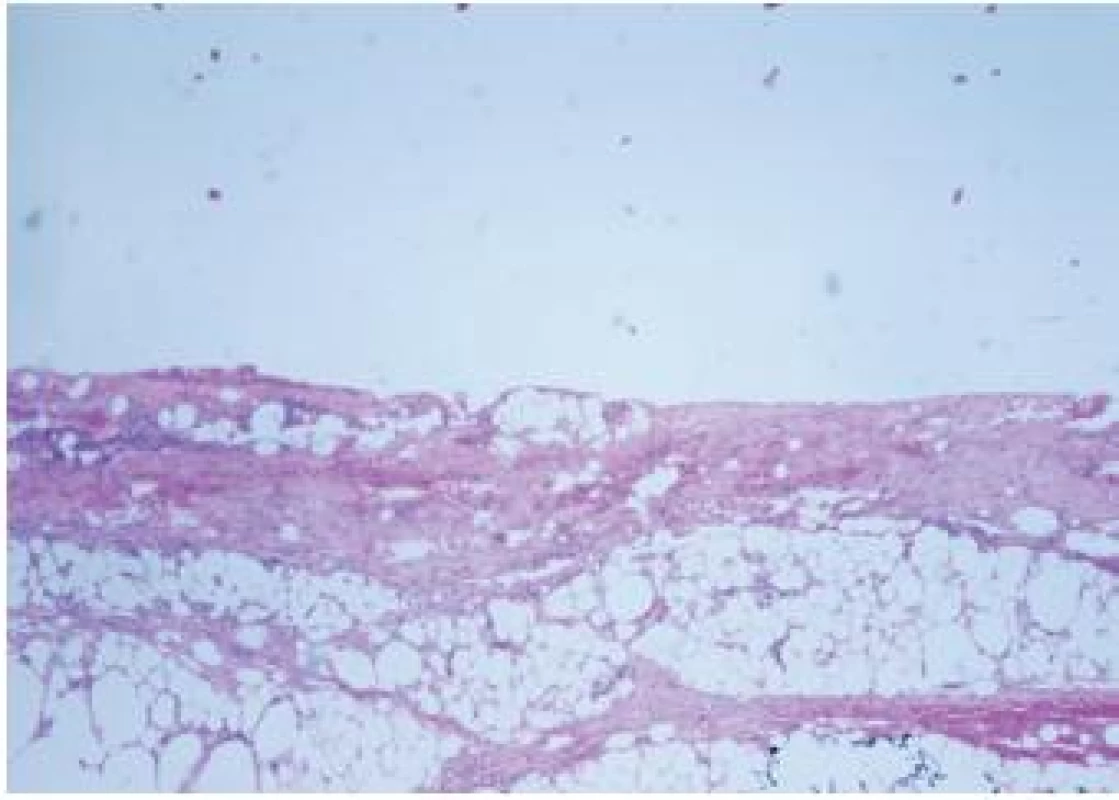
Obrázek z archivu autora Do II. stupně traumatizace, TDD II – v mikroskopickém obraze jsou typické mírné nerovnosti okraje, menší trhliny – jsme zařadili vzorky se součtem tři a čtyři body (viz obrázek 3)
Image 3. Stupeň TDD II – mírné nerovnosti okraje, menší trhliny 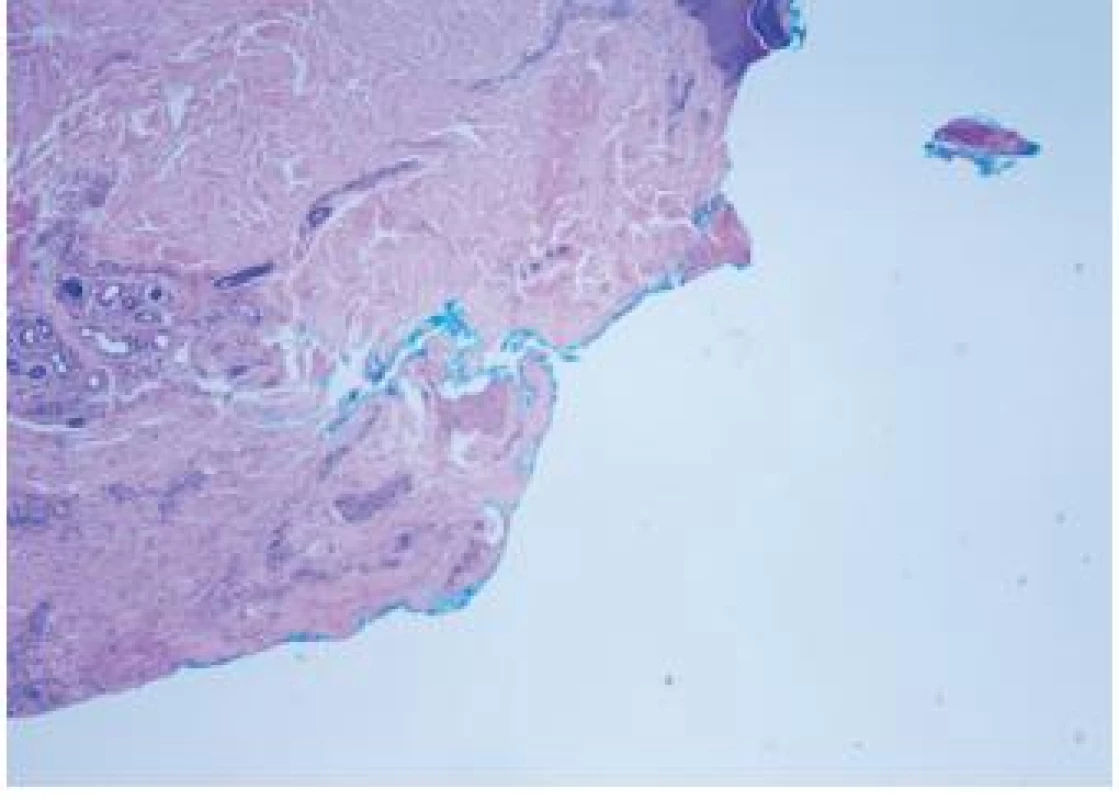
Obrázek z archivu autora Do III. stupně traumatizace, TDD III – v histologickém hodnocení typicky velké zhmoždění tkáně, velké a hluboké trhliny – jsme zařadili vzorky se skóre pět a šest bodů (viz obrázky 4 a 5)
Image 4. Stupeň TDD III – velké zhmoždění tkáně, velké trhliny 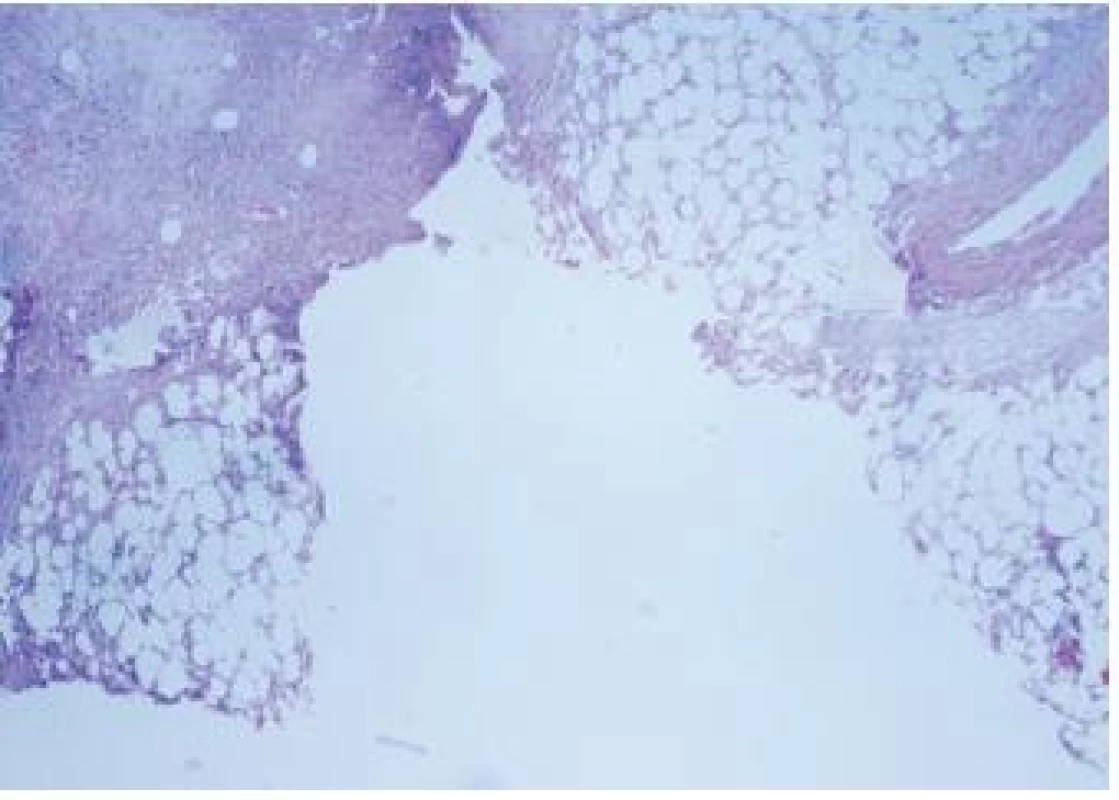
Obrázek z archivu autora Image 5. Stupeň TDD III – velké zhmoždění tkáně, velké trhliny 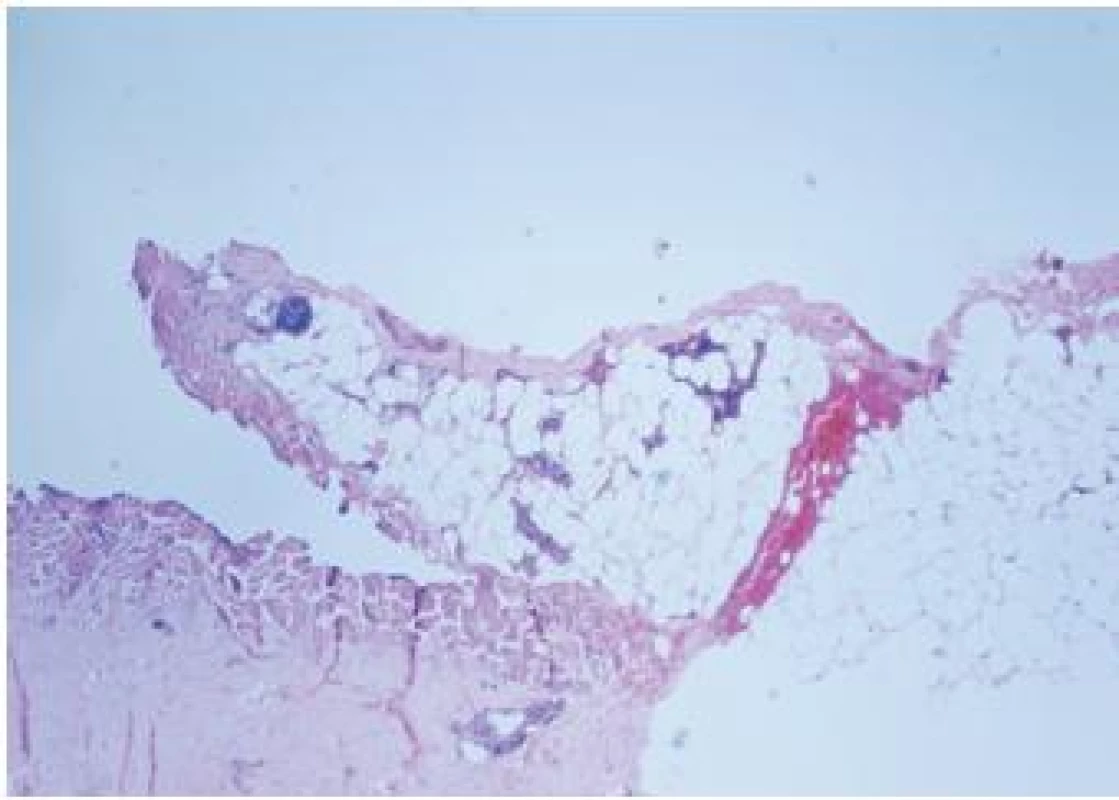
Obrázek z archivu autora Hodnocení preparátů bylo prováděno „naslepo“, hodnotící lékař nevěděl, jakou technikou byl ten který vzorek ošetřen. Jednotlivé tkáňové vzorky dosáhly skóre minimálně jeden a maximálně šest bodů. Jako nejčastější marker poškození tkáně na povrchu rány zaznamenal patolog ve 128 zpracovaných řezech rozdrcení tkáně (115 řezů; 30,6 %), mikroskopickou nerovnost okraje (96 řezů; 25,6 %) a poškození spodiny do hloubky více než 0,5 mm (81 řezů; 21,6 %). Hematom na spodině a v okrajích popsal u 40 řezů (10,7 %), nejméně často byly přítomny viditelné trhliny v cévách (29 řezů; 7,7 %) a sekundární nekrózy na spodině rány (14 řezů; 3,8 %). Rozložení četnosti sledovaných markerů je patrné v tabulce 3 a na obrázku 6. Podle výskytu sledovaných markerů byla jednotlivým řezům přiřazena příslušná hodnota TDD, která byla následně zanesena do hodnotící tabulky 4.
Table 3. Přehled markerů tkáňového poškození na testovaných tkáňových vzorcích 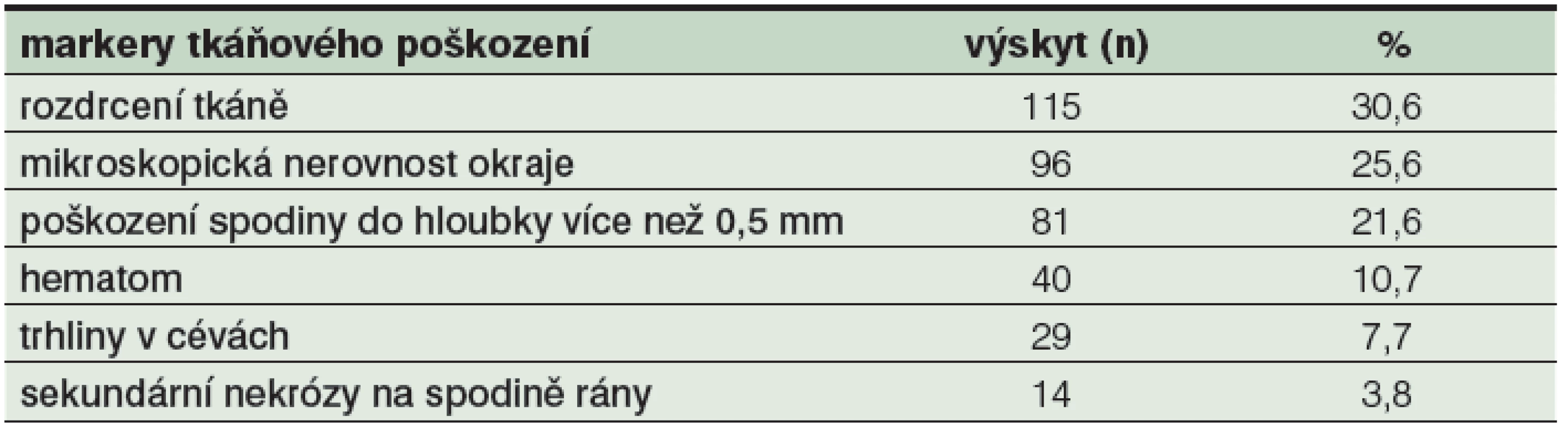
Image 6. Přehled markerů tkáňového poškození na testovaných tkáňových vzorcích 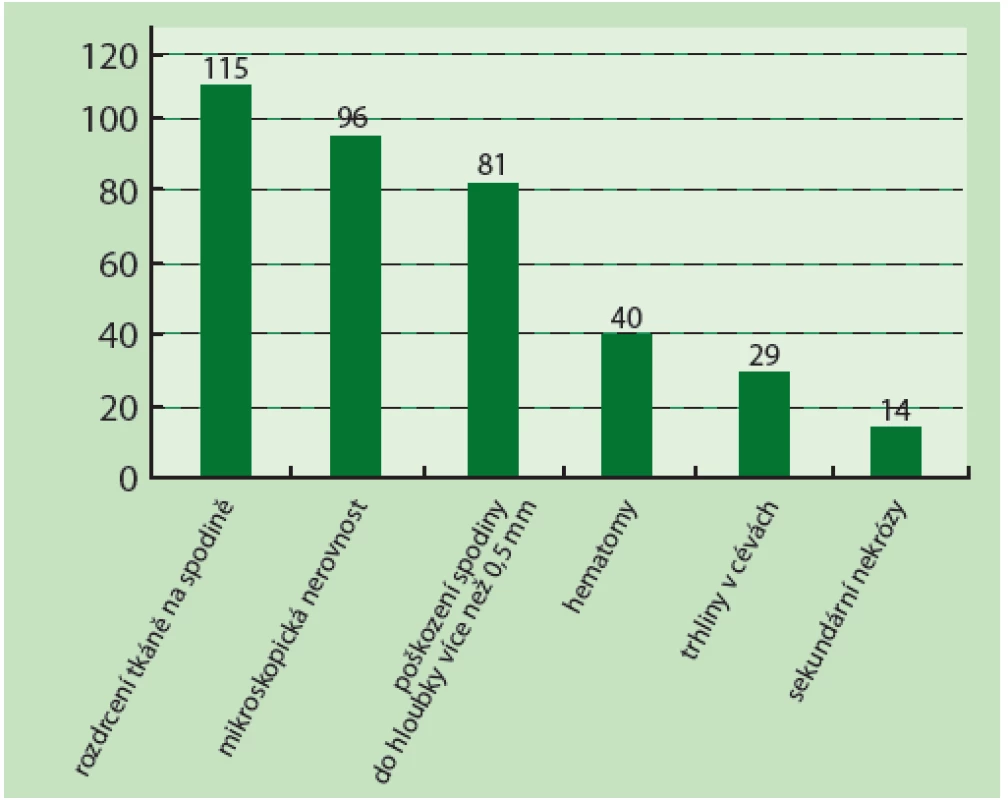
Obrázek z archivu autora Table 4. Vyjádření rozložení stupňů TDD v jednotlivých skupinách débridementu V, N, E a S1 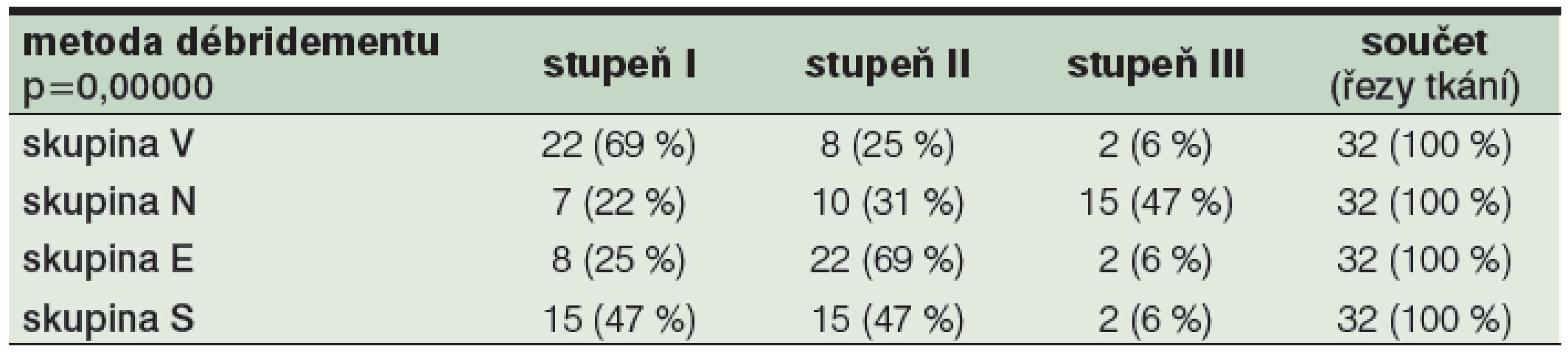
1 Skupina V – débridement provedený hydrochirurgickou metodou Versajet skupina N – débridement proveden pomocí chirurgických nůžek skupina E – débridement proveden pomocí ekeltrokauteru skupina S – débridement proveden pomocí skalpelu Výsledky
Spodina rány ošetřená hydrochirurgickou metodou (skupina V) vykazovala nejčastěji stupeň tkáňového poškození TDD I (22; tj. 69 %). U spodiny rány ošetřené metodou nůžky (skupina N) jsme pozorovali nejčastěji stupeň tkáňového poškození TDD III (15; tj. 47 %). Spodina rány ošetřená metodou elektrokauter (skupina E) vykazovala nejčastěji stupeň tkáňového poškození TDD II (22; tj. 69 %) a u rány ošetřené metodou skalpel (skupina S) jsme zaznamenali stejné zastoupení stupně poškození TDD I a TDD II (15 a 15; tj. dohromady 93 %). Detaily viz tabulka 4: Vyjádření rozložení stupňů TDD. Stupeň traumatizace TDD I měl nejvyšší četnost ve skupině vzorků ošetřených Versajetem. Stupeň traumatizace TDD II měl nejvyšší četnost ve skupině tkáňových vzorků ošetřených elektrokauterem. Stupeň traumatizace TDD III měl nejvyšší četnost ve skupině vzorků ošetřených chirurgickými nůžkami. Podíl testovaných metod débridementu na jednotlivých stupních TDD ukazují tabulka 5 a obrázek 7.
Table 5. Podíl jednotlivých skupin V, N, E a S na rozložení stupňů TDD 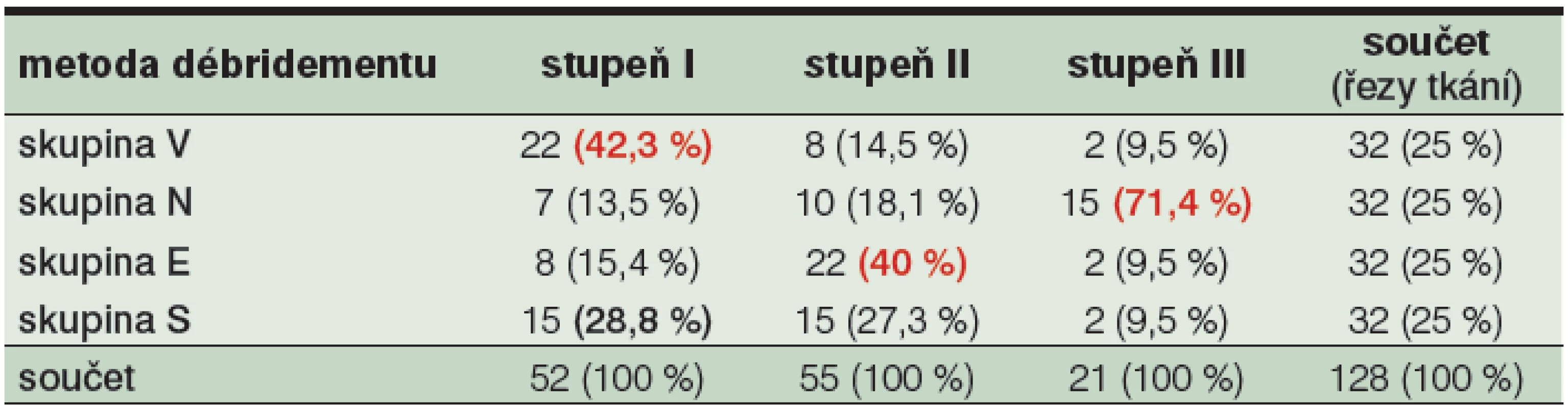
Image 7. Podíl jednotlivých skupin V, N, E a S na rozložení stupňů TDD 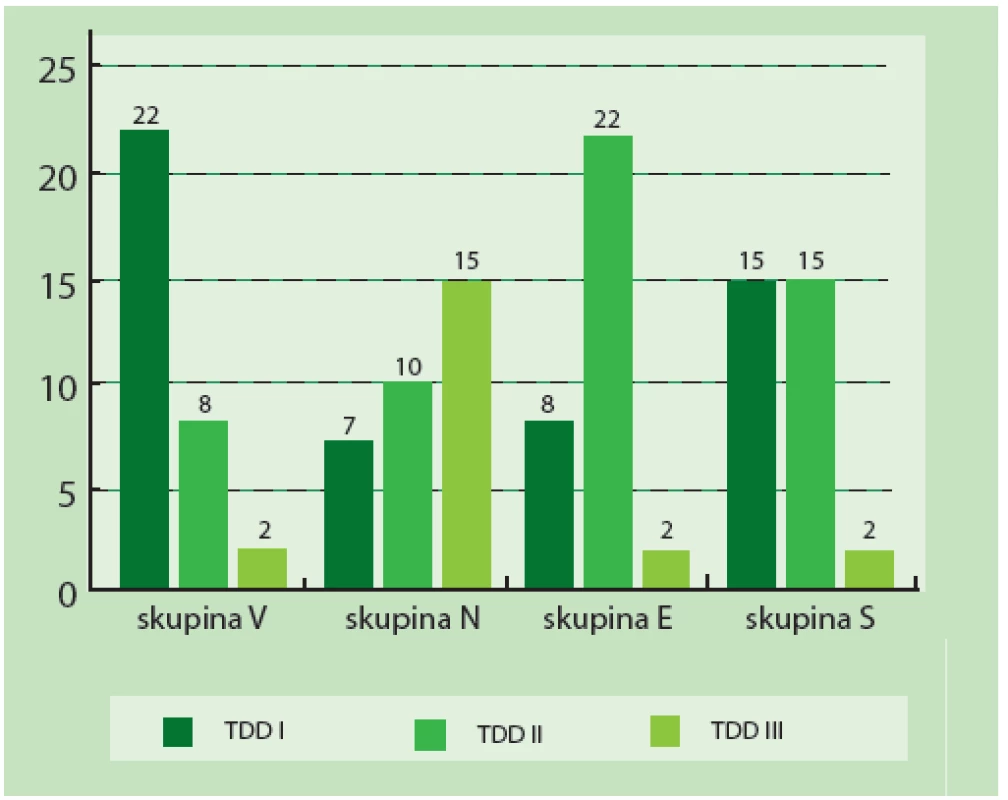
Obrázek z archivu autora Míru traumatizace rány při použití zkoumaných technik débridementu můžeme vizualizovat také pomocí tzv. průměrného skóre traumatizace (ATDD), které zohledňuje nejen zastoupení jednotlivých stupňů TDD I, II a III v souboru, ale i významnost histopatologických změn pro zhodnocení dopadu příslušné techniky débridementu na ránu. Abychom rozlišili intenzitu poškození tkáně v jednotlivých kategoriích TDD I, II a III, přiřadili jsme každé kategorii specifický kTDD koeficient: I. stupni poškození přísluší koeficient kTDDI=1, II. stupni poškození koeficient kTDDII=2 a III. stupeň poškození získal koeficient kTDDIII=3. Ve výpočtu ATDD byla zohledněna incidence jednotlivých stupňů a hodnota kTDD koeficientu. Hodnota ATDD konkrétní metody débridementu je dána součtem součinu počtu jednotlivých TDD stupňů a příslušného koeficientu poškození tkáně kTDDI, kTDDII a kTDDIII, který vydělíme počtem hodnocených vzorků (n=32). Čím vyšší hodnota ATDD skóre, tím rozsáhlejší bylo poškození tkání zkoumaných vzorků. S ohledem na skóre ATDD nejlepších výsledků (tj. nejnižšího průměrného stupně traumatizace) dosáhla testovaná metoda „V“ následovaná metodou „S“ a technikou „E“. Nejhorší výsledky (tj. nejtěžší histopatologické změny na povrchu rány způsobené traumatizací rány při débridementu) jsme zaznamenali u metody „N“ – débridement provedený nůžkami (viz tabulka 6).
Table 6. Průměrné skóre traumatizace tkáně1 v jednotlivých skupinách débridementu2 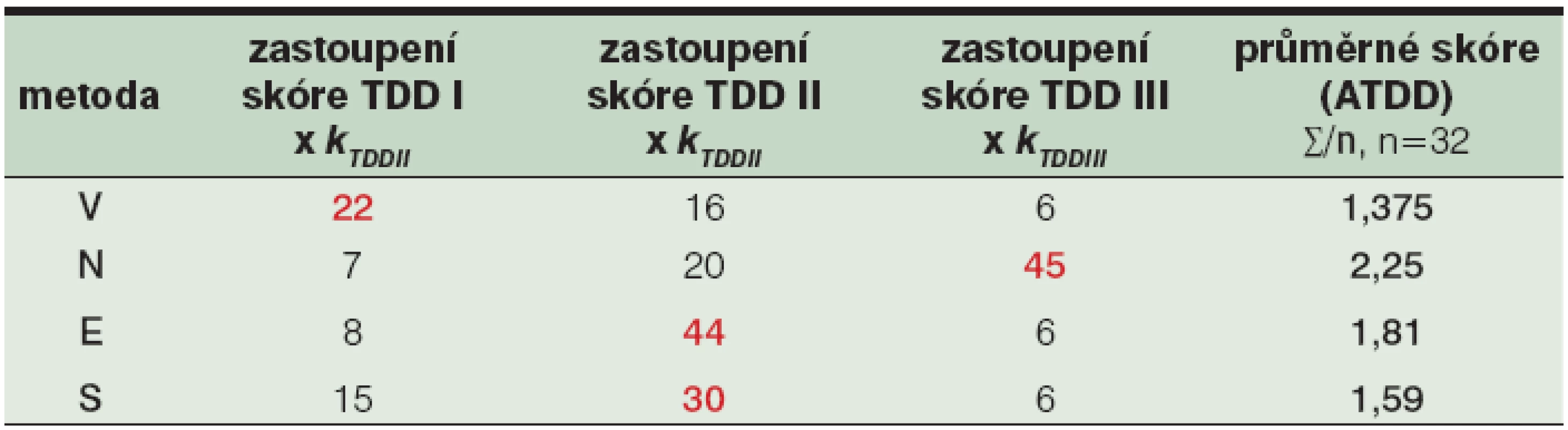
1 po započítání koeficientu stupně poškození tkáně 2 skupina V – débridement provedený hydrochirurgickou metodou Versajet; skupina N – débridement proveden pomocí chirurgických nůžek; skupina E – débridement proveden pomocí elektrokauteru; skupina S – débridement proveden pomocí skalpelu Shrnutí výsledků a statistická analýza
V experimentu jsme prokázali, že unikátní skórovací systém TDD je schopen jednoznačně definovat stupeň poškození testovaného vzorku tkáně definovanou formou débridementu a že TDD lze použít k validaci míry traumatizace. Dále jsme prokázali, že existuje statisticky významný rozdíl v intenzitě poškození spodiny modelu rány při použití čtyř metod ostrého débridementu: skalpelu, nůžek, elektrokauteru a hydrochirurgického nástroje Versajet (viz tabulka 7). Při vzájemném porovnání stupně traumatizace testovaných vzorků tkáně jsme potvrdili, že nůžky i elektrokauter vykazují signifikantně vyšší míru traumatizace než hydrochirurgická metoda Versajet (viz tabulka 7). Při porovnání stupně traumatizace tkáně použitím skalpelu a hydrochirurgického nástroje Versajet nebyl nalezen statisticky signifikantní rozdíl hodnot TDD, stejně jako při porovnání výsledků débridementu elektrokauterem a skalpelem (viz tabulka 7). Débridement za použití nůžek vedl signifikantně k vyššímu stupni traumatizace než débridement s využitím elektrokauteru i skalpelu. Na základě analýzy rozložení TDD v testovaných skupinách a porovnání výsledků jednotlivých typů débridementu navzájem považujeme débridement provedený hydrochirurgickou metodou Versajet za nejméně traumatizující ze všech testovaných forem débridementu rány. Nejvyšší míra traumatizace byla prokázána v případě débridementu tkáňových vzorků ošetřených pomocí chirurgických nůžek.
Table 7. Shrnutí výsledků statistické analýzy testovaných metod débridementu 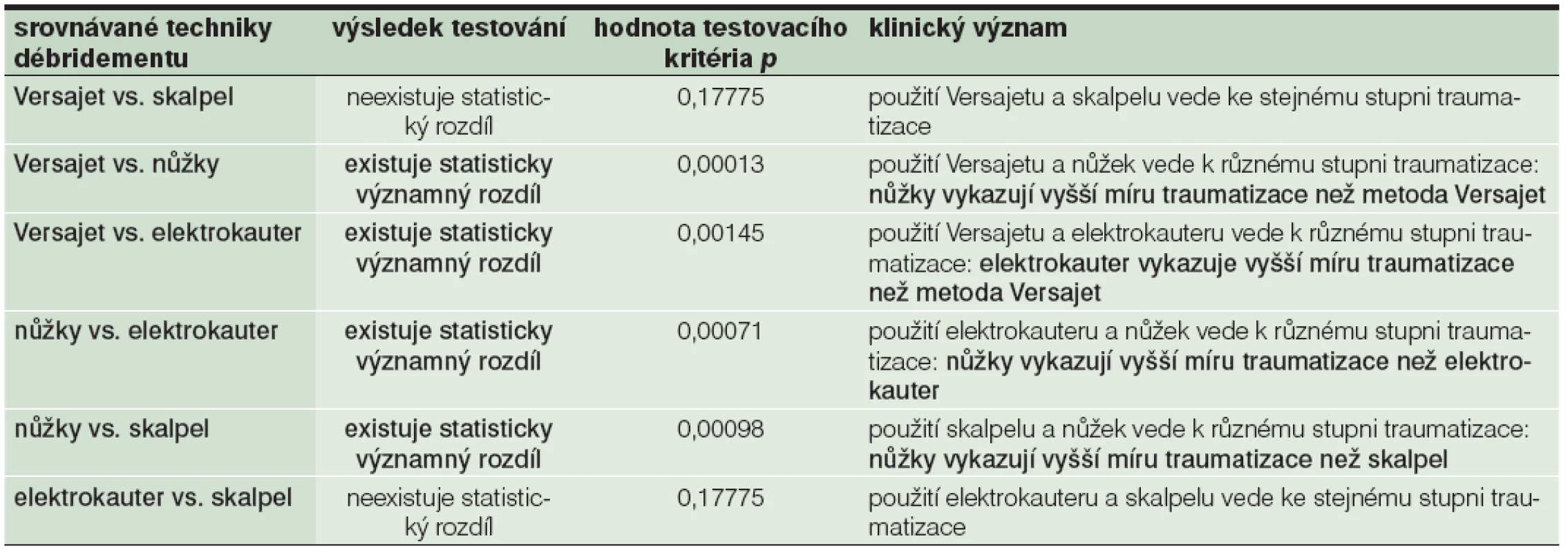
Závěr
Na základě nově etablovaného klasifikačního systému TDD, tvořeného třemi stupni traumatizace, byl potvrzen statisticky významný rozdíl (p=0,00014) v míře traumatizace testované tkáně při použití čtyř metod ostrého débridementu a námi navržený systém TDD lze tedy využít k posouzení míry traumatizace testované tkáně. Zároveň byla identifikována nejvíce a nejméně traumatizující metoda débridementu ran. Ve výzkumu jsme prokázali, že hydrochirurgický débridement provedený metodou Versajet vykazuje na spodině testované ulcerace ze všech testovaných modalit nejméně histologických markerů traumatizace. V traumatizaci tkáně skalpelem, chirurgickými nůžkami, elektrokauterem a handpiecem Versajetu existují statisticky signifikantní rozdíly (p=0,00000). Míra traumatizace tkáně hydrochirurgickým débridementem je statisticky signifikantně menší než v případě použití chirurgických nůžek a elektrokauteru (p=0,00112; p=0,00005). Rozdíl v traumatizaci tkáně skalpelem a nástrojem Versajet není statisticky signifikantní (p=0,17404). Statistická analýza výsledků experimentu potvrdila, že při použití chirurgických nůžek bylo dosaženo největší úrovně traumatizace spodiny rány (p<0,0001). Nejmenší míra traumatizace byla dosažena v případě débridementu modelové rány hydrochirurgickou metodou (ATDDVersajet=1,375 versus ATDDnůžky=2,25).
MUDr. Jan Stryja
Komplexní kardiovaskulární centrum
Nemocnice Podlesí a.s.
Konská 453
739 61 Třinec
e-mail: jan.stryja@atlas.cz
Sources
Goode, P. S. Consensus on wound débridement: a US perspective. Eur Tissue Repair Soc 2, 4 : 104, 1995.
Lebrun, E., Tomic-Canic, M., Kirsner, R. S. The role of surgical débridement in healing of diabetic foot ulcers. Wound Repair Regen 18, 5 : 433–438, 2010.
National Institute for Clinical Excellence. Guidance for the use of debriding agents for difficult to heal surgical wounds. London: NICE, 2001. (NICE 2001)
Stryja, J. How to rate the wound débridement trauma? Journal Eur Wound Management Association (EWMA) 12, 1 : 7–12, 2012.
Tenenhaus, M., Bhavsar, D., Rennekampff, H. O. Treatment of deep partial thickness and indeterminate depth facial burn wounds with water-jet débridement and a biosynthetic dressing. Injury 38, Suppl 5: S38–S45, 2007.
Labels
Surgery Nurse Home nurse
Article was published inWound Healing

2014 Issue 1-
All articles in this issue
- Altrazeal – nová forma polyakrylátového krytí v klinické praxi
- Otakar Kukula (2. 2. 1867–11. 8. 1925)
- Předplatné zdarma
-
XII. celostátní kongres s mezinárodní účastí: Mezioborová spolupráce při léčbě ran a kožních defektů
Pardubice, 2014 - Program
- Abstrakta XI. Celostátního kongresu mezioborové spolupráce při léčbě ran a kožních defektů s mezinárodní účastí (Pardubice)
- Traumatizace rány při chirurgickém débridementu – experimentální studie
- Wound Healing
- Journal archive
- Current issue
- Online only
- About the journal
Most read in this issue- Altrazeal – nová forma polyakrylátového krytí v klinické praxi
- Traumatizace rány při chirurgickém débridementu – experimentální studie
- Abstrakta XI. Celostátního kongresu mezioborové spolupráce při léčbě ran a kožních defektů s mezinárodní účastí (Pardubice)
- Otakar Kukula (2. 2. 1867–11. 8. 1925)
Login#ADS_BOTTOM_SCRIPTS#Forgotten passwordEnter the email address that you registered with. We will send you instructions on how to set a new password.
- Career

